Practical Intro to Reinforcement Learning
I remember the first time I stumbled upon reinforcement learning. It felt like unlocking a new level in a game, where algorithms learn by trial and error, just like us. Unlike supervised learning, RL doesn't rely on labeled datasets. It learns from the consequences of its actions. First, I'll compare RL to supervised learning, then dive into its real-world applications, especially in games. I'll walk you through value-based methods like Q-learning and policy-based methods, showing how these approaches are transforming massive language models. In the end, you'll see how three key ways of using RL to fine-tune large language models deliver impressive results.
I remember the first time I stumbled upon reinforcement learning; it was like entering a new level in a video game. Algorithms learning through trial and error—fascinating, right? What sets RL apart from supervised learning is its independence from labeled datasets. First, I connect this concept to supervised learning to set the stage. Then, I show you RL's real-world applications, where it especially shines in games. I'll guide you through value-based methods like Q-learning and policy-based methods. And watch out, I had to adjust my expectations when working with these methods on large language models. Three key approaches emerge for fine-tuning these massive models with RL, and the results are often mind-blowing. So, ready to dive into this exciting world?
Understanding Reinforcement Learning
So here's the deal with reinforcement learning (RL) — it's like diving into a whole new world compared to supervised learning. We're talking about agents, environments, actions, and rewards. Unlike supervised learning which relies on labels, RL learns from direct interaction with the environment. Think of an agent in a video game trying out various strategies to get the highest score possible. That's RL: try, fail, adjust, and try again.
The key components here are the agent (the decision-maker), the environment (the world around the agent), the policy (the agent's strategy), the reward signal (what motivates the agent), and the value function (evaluation of future actions). It's an iterative process where the agent learns through trial and error. I've often seen projects fail simply because teams underestimated the time needed for the agent to truly refine its strategy.
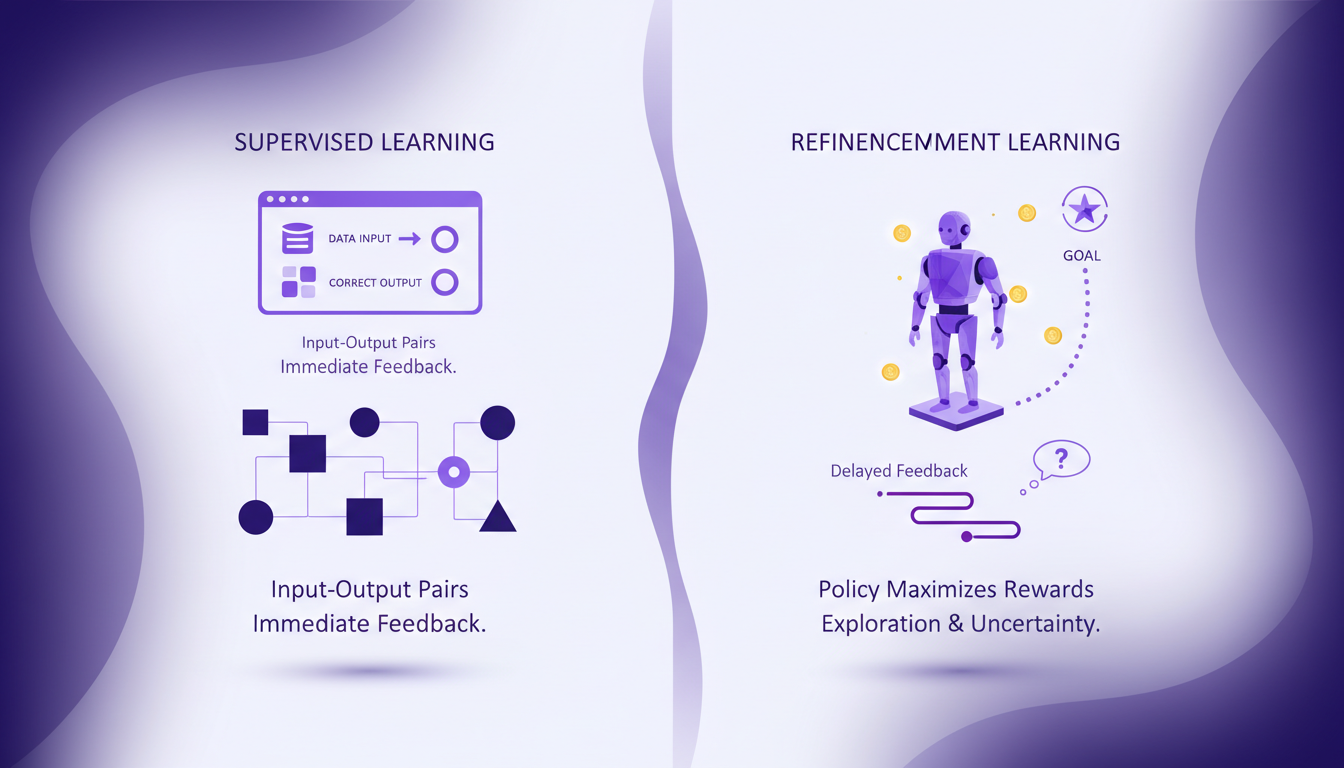
Reinforcement vs Supervised Learning
When I compare RL to supervised learning, the most glaring difference is the reliance on data. Supervised learning needs tons of labeled data, input-output pairs, to function. RL, on the other hand, focuses on finding a policy that maximizes cumulative rewards. But watch out, it's a resource hog. I've often seen RL projects consume more computing power than expected, especially because feedback is often delayed, adding complexity to learning.
In terms of trade-offs, RL is undeniably more flexible. But this flexibility comes at a cost: more computational resources and time. To choose between the two, you really have to weigh the need for flexibility against resource constraints. For more details, check out this comprehensive comparison.
Applications in Games and Beyond
Where RL truly shines is in dynamic environments like games. Take AlphaGo, which surpassed Grandmaster level. But that's not all. RL finds its place in robotics, autonomous vehicles, and personalized recommendations as well. It optimizes complex decision-making processes impressively. However, watch out for high computational costs and data requirements. I've seen many projects fail due to these hidden costs.
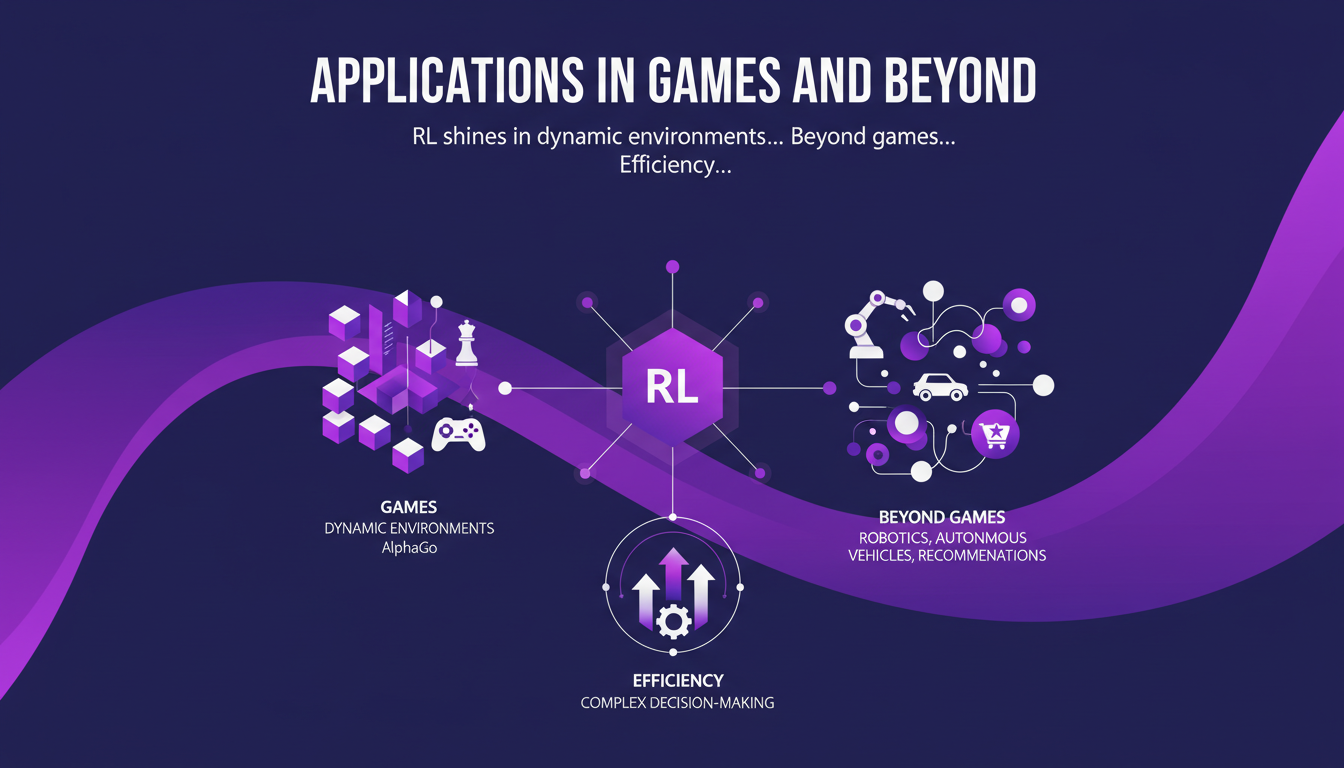
So whether it's for games like Go or more practical tasks like stock management, RL has a real impact. Notable examples include AlphaGo and OpenAI's Dota 2 bot. For more practical applications, check out our guide on deploying multimodal capabilities.
Value-based vs Policy-based Methods
Value-based methods such as Q-learning focus on evaluating the value of possible actions. In parallel, policy-based methods like REINFORCE directly optimize the policy. The Actor-Critic approach combines these two for better stability and performance. Choosing the right method depends on the problem at hand and the available resources.

I've often seen projects adopt a method without understanding the trade-offs. For instance, Q-learning is powerful but can be computationally heavy. REINFORCE, while more straightforward, may require many tries to converge. To explore these methods, take a look at our practical guide on diffusion in ML.
Reinforcement Learning with Large Language Models
Large language models (LLMs) leverage RL for fine-tuning, enhancing responses and efficiency. The three key ways to do this are reward shaping, policy optimization, and environment simulation. But watch out, managing token usage and computational overhead is a real challenge. Yet, the benefits are clear: more adaptive and context-aware language models.
When I first started working with these models, I often underestimated resource consumption. With over 100,000 tokens in modern models' vocabulary, it's crucial to manage resources well. To see how these techniques apply to voice cloning, check out our article on Qwen TTS.
So, here's what I really got out of reinforcement learning (RL):
- First off, RL is a real game changer for tackling complex problems, especially when you stack it against supervised learning. But watch out for the challenges, especially as you scale.
- Then, think about Q-learning. It's a concrete example of a value-based method that can transform how we train language models, even those with vocabularies of 100,000 tokens.
- Finally, RL isn't just for games. Its applications reach far beyond, and with the right methods (value-based or policy-based), you can really make a difference.
Looking ahead, I'm convinced these RL tools will keep evolving and transforming our AI projects. But remember the trade-offs: optimization and computation time can become a headache.
Ready to dive deeper? I really suggest you start experimenting with RL frameworks. Share your experiences, and together, let's build smarter solutions. Check out the video "Reinforcement Learning: A (practical) introduction" on YouTube for more deep dives into this fascinating topic: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=3vFISl7qMFI.
Frequently Asked Questions

Thibault Le Balier
Co-fondateur & CTO
Coming from the tech startup ecosystem, Thibault has developed expertise in AI solution architecture that he now puts at the service of large companies (Atos, BNP Paribas, beta.gouv). He works on two axes: mastering AI deployments (local LLMs, MCP security) and optimizing inference costs (offloading, compression, token management).
Related Articles
Discover more articles on similar topics
Translate Gemma: Multimodal Capabilities in Action
I've been diving into Translate Gemma, and let me tell you, it's a real game changer for multilingual projects. First, I set it up with my existing infrastructure, then explored its multimodal capabilities. With a model supporting 55 languages and training data spanning 500 more, it's not just about language—it's about how you deploy and optimize it for your needs. I'll walk you through how I made it work efficiently, covering model variant comparisons, training processes, and deployment options. Watch out for the model sizes: 4 billion, 12 billion, up to 27 billion parameters—this is heavy-duty stuff. Ready to see how I used it with Kaggle and Hugging Face?
Clone Any Voice for Free: Qwen TTS Revolutionizes
I remember the first time I cloned a voice with Qwen TTS—it was like stepping into the future. Imagine having such a powerful tool, and it's open source, right at your fingertips. This isn't just theory; it's about real-world application today. Last June, Qwen announced their TTS models, and by September, the Quen 3 TTS Flash with multilingual support was ready. For anyone interested in voice cloning and multilingual speech generation, this is a true game changer. With models ranging from 0.6 billion to 1.7 billion parameters, the possibilities are vast. But watch out, there are technical limits to be mindful of. In this article, I'll guide you through multilingual capabilities, open-source release, and emotion synthesis. Get ready to explore how you can leverage this tech today.
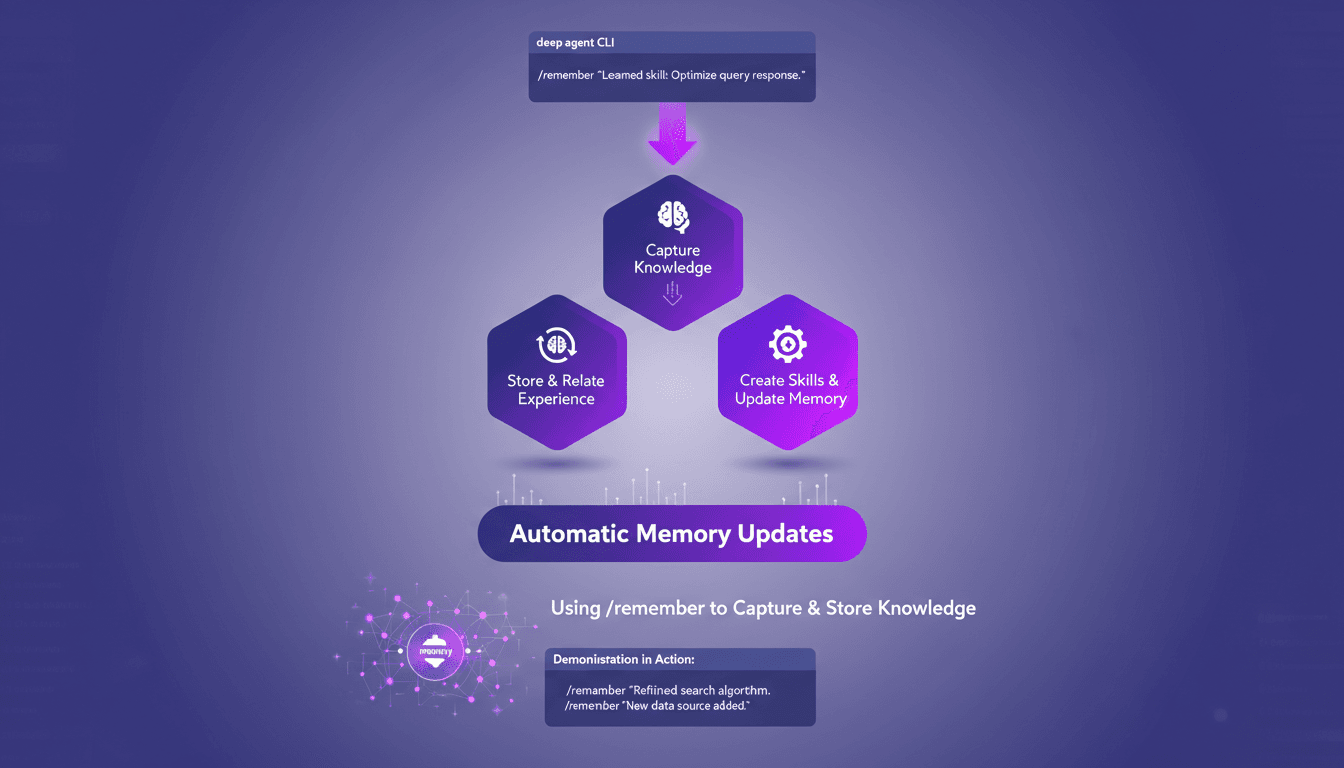
Mastering /remember: Deep Agent Memory in Action
I've spent countless hours tweaking deep agent setups, and let me tell you, the /remember command is a game changer. It's like giving your agent a brain that actually retains useful information. Let me show you how I use it to streamline processes and boost efficiency. With the /remember command in the deep agent CLI, you can teach agents to learn from experience. Let's dive into how this works and why it's a must-have in your toolkit.
Mastering Diffusion in ML: A Practical Guide
I've been knee-deep in machine learning since 2012, and let me tell you, diffusion models are a game changer. And they're not just for academics—I'm talking about real-world applications that can transform your workflow. Diffusion in ML isn't just a buzzword. It's a fundamental framework reshaping how we approach AI, from image processing to complex data modeling. If you're a founder or a practitioner, understanding and applying these techniques can save you time and boost efficiency. With just 15 lines of code, you can set up a powerful machine learning procedure. If you're ready to explore AI's future, now's the time to dive into mastering diffusion.
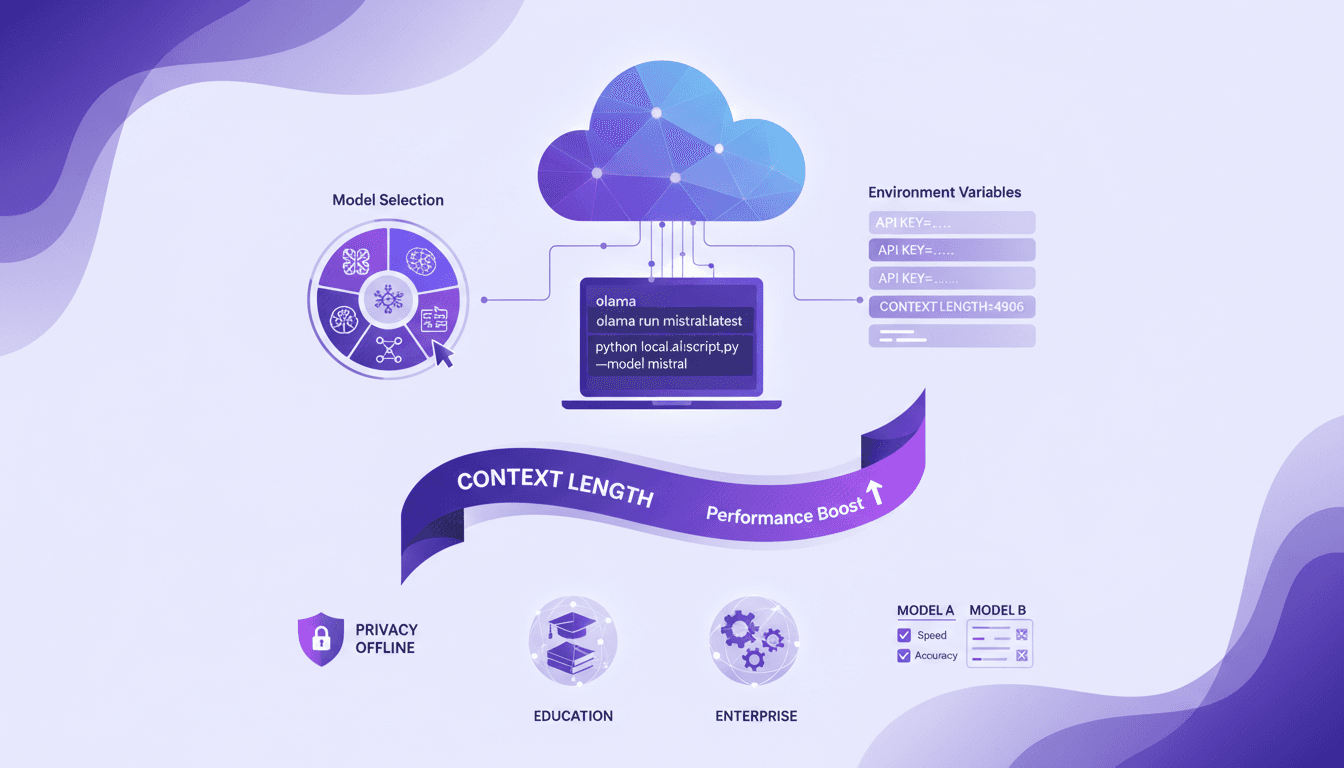
Run Cloud Code Locally with Olama: Tutorial
I've been running cloud code locally to boost efficiency and privacy, and Olama has been a real game changer. Imagine handling AI models with 4 billion parameters, all without leaving your desk. I'll show you how I set it up, from model selection to tweaking environment variables, and why it’s a game changer for education and enterprise. But watch out for context limits: beyond 100K tokens, things get tricky. By using Olama, we can compare different AI models for local use while ensuring enhanced privacy and offline capabilities. The goal here is to give you a practical, hands-on look at how I orchestrate these technologies in my professional life.