Run Cloud Code Locally with Olama: Tutorial
I've been running cloud code locally to boost efficiency and privacy, and Olama has been a real game changer. Imagine handling AI models with 4 billion parameters, all without leaving your desk. I'll show you how I set it up, from model selection to tweaking environment variables, and why it’s a game changer for education and enterprise. But watch out for context limits: beyond 100K tokens, things get tricky. By using Olama, we can compare different AI models for local use while ensuring enhanced privacy and offline capabilities. The goal here is to give you a practical, hands-on look at how I orchestrate these technologies in my professional life.
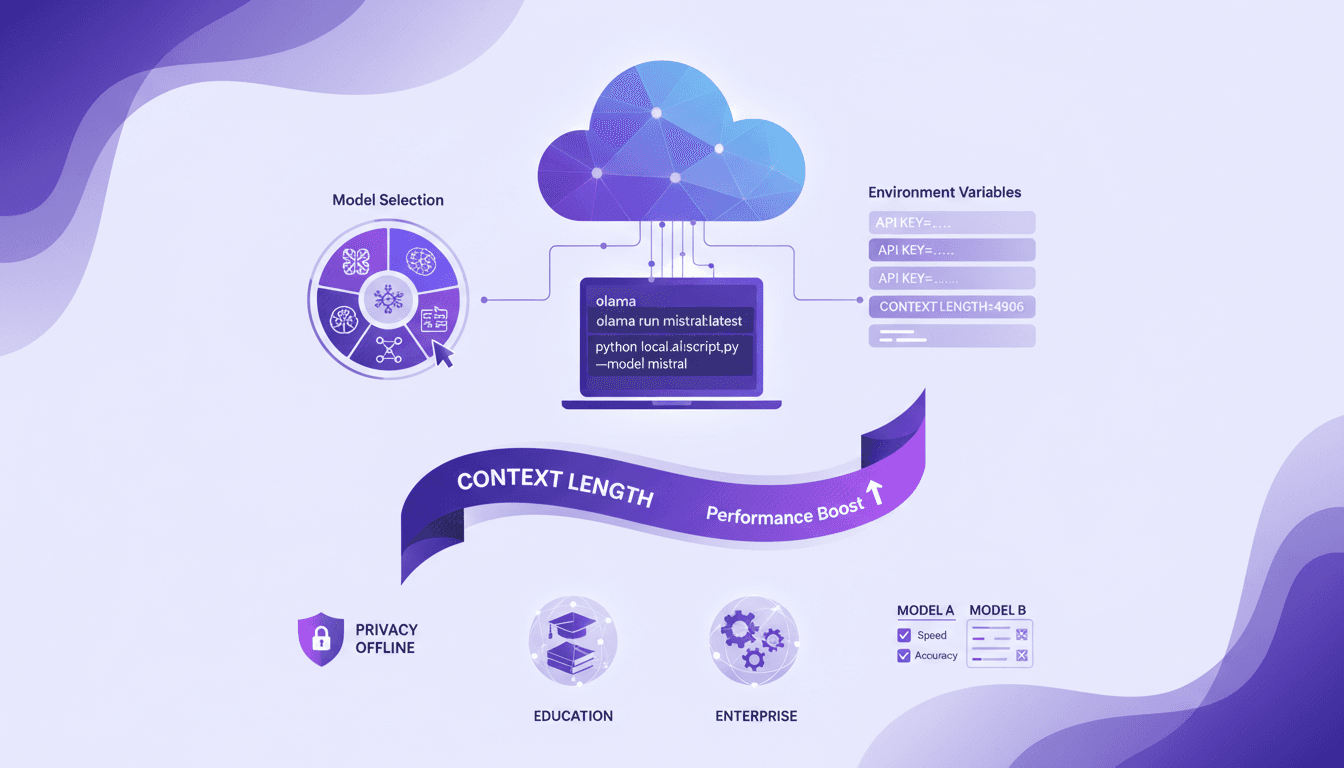
Running cloud code locally feels like having a superpower right at your desk — and Olama is the tool that made it possible for me. I started dabbling with AI models that boast 4 billion parameters, and let me tell you, it's a game changer for both educational and enterprise applications. I'm going to walk you through how I set everything up, step by step, from selecting models to configuring environment variables. But beware of pitfalls: go beyond 100K tokens, and it can turn into a nightmare. By using Olama, we can not only compare different AI approaches for local use, but also enjoy enhanced privacy and offline capabilities. I'll even share the technical setup and commands I use to orchestrate it all. It's had a direct impact on my daily efficiency, and I'm confident it can help you too.
Setting Up Your Local Environment with Olama
First things first, if you want to run AI models locally without spending a dime, Olama is your go-to. I found myself downloading and installing Olama on my machine, and I recommend you do the same. Make sure you have the latest version to avoid any hiccups. Once installed, open Olama and configure the environment variables for optimal performance. For instance, Olama serves models locally on port 1434. This is crucial, trust me, because without it, you'll have trouble getting your model to work with Claude Code.
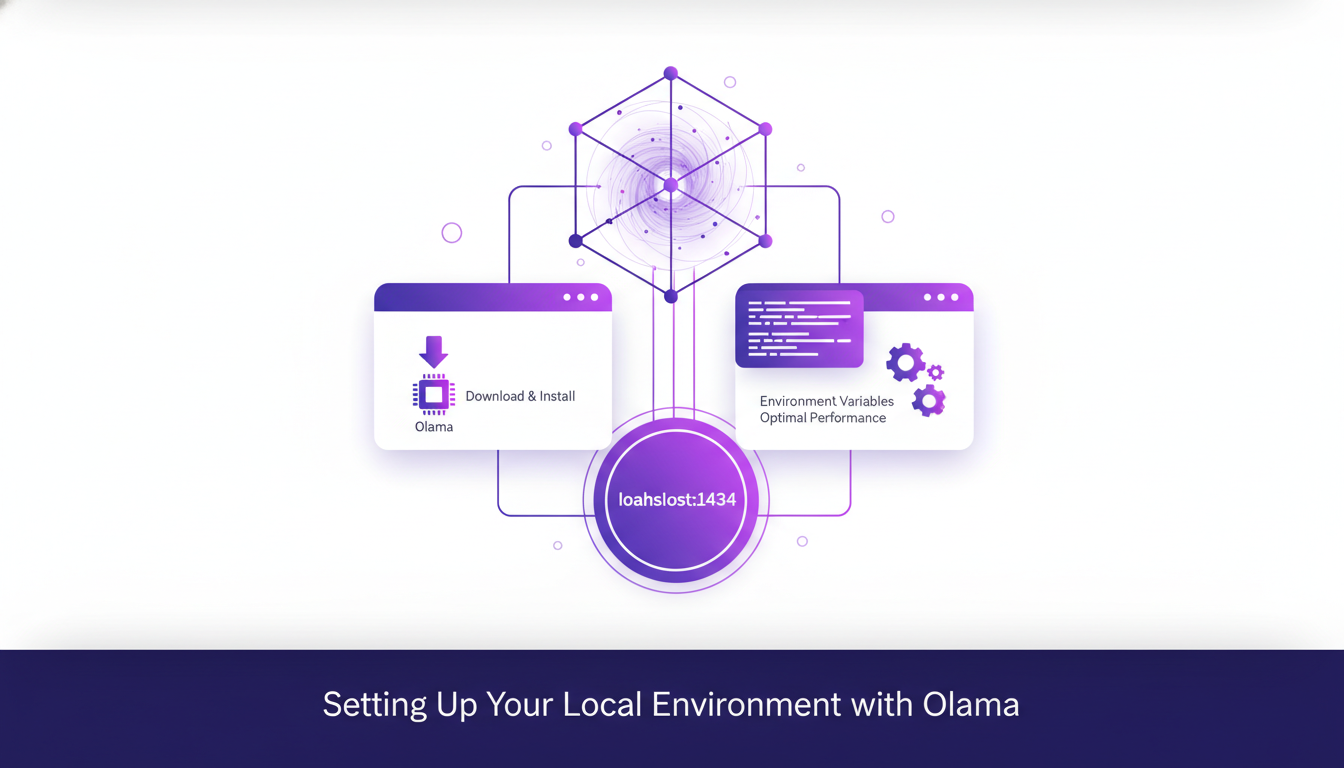
Setup issues can arise, so be vigilant. I ran into a few snags with environment variables not being set properly. Ensure you correctly define your anthropic o token and anthropic base URL. If Olama isn't working as expected, check that the model is being served on port 1434. Without this, your cloud code won't access the model.
Selecting and Running AI Models Locally
Once your environment is set up, the next step is choosing the right model. With Olama, you have several models to choose from, like the GLM 4.7 flash, which is 19 GB with 4 billion parameters. This model is ideal if you have a powerful machine, but watch out, don't download this on an old PC! Personally, I opted for the Quen 3 model with its 4 billion parameters. You don't need a beast of a machine for this one, but it still packs a punch.
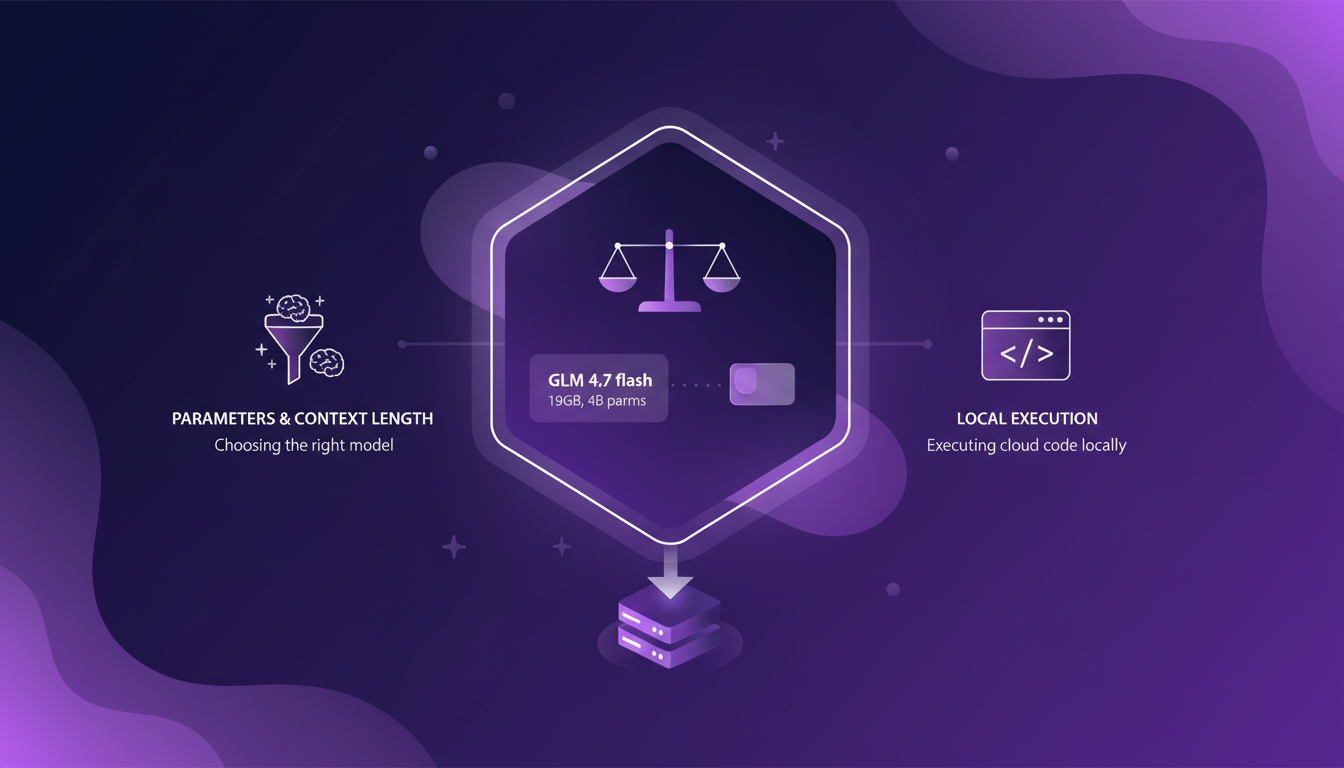
Consider executing cloud code commands locally to test the efficiency of your chosen model. I personally ran scripts that counted the number of files in my root folder. It took 2 minutes 23 seconds to do this, a bit slow, but it gave me the right answer. The choice of model directly impacts the tooling and thinking capabilities.
The Role of Context Length in AI Model Performance
Context length is crucial. If you're asking complex questions, you need a model with an adequate context length, like 32,000 or 64,000 tokens. This directly impacts the model's "thinking" capability. I've seen models fail miserably because the context length was too short. So, balancing context length with resources is essential.
In the real world, use a longer context for complex tasks, but keep in mind it can consume a lot of memory and slow things down.
Applications of Local AI Models in Education and Enterprise
Local AI models aren't just a geek's toy. In education, they can transform how we approach learning. Imagine a teacher using a local AI model to generate personalized exercises. That's a game changer!
In the enterprise world, privacy and control are major benefits. You don't want your sensitive data exposed to cloud services, do you? With Olama, you keep everything local without sacrificing performance. However, be aware of technical limitations: local implementation requires adequate resources and some technical know-how.
Technical Commands and Workflow with Olama
I've orchestrated my workflow to maximize efficiency and cut costs. The key is understanding the commands to execute. For example, to set up Olama, you start by opening your terminal and running specific commands according to your operating system.
Here's a quick rundown:
- Ensure cloud code is added to your path.
- Correctly set your environment variables.
- Avoid common pitfalls like forgetting to run Olama on the correct port.
Integration with existing systems can be a headache, but once everything is in place, the efficiency gains are immediate. Don't underestimate the importance of these steps for smooth operation.
I dove into setting up AI models locally with Olama, and the advantages became clear fast: enhanced privacy and increased efficiency. But watch out, choosing the right models is critical. For example, with the 19 GB GLM 4.7 flash model boasting 4 billion parameters, you can really feel the power, but also the need to optimize your environment. I also learned that context length is crucial for performance, so don't overlook that.
- Model Selection: Choosing the right tools and models is essential to maximize performance.
- Environment Variables Setup: A key step to get your local AI models running smoothly.
- Execution Time: Counting files in the root folder took 2 minutes 23 seconds, a good benchmark to evaluate your own performance.
Looking ahead, I see a multitude of possibilities to explore, whether in education or enterprise. So, ready to get started? Dive into the setup and explore the potential of local AI models in your context. For deeper insights, I recommend watching the full video: Claude Code for Free using Local AI Models. You'll find practical tips to push even further.
Frequently Asked Questions

Thibault Le Balier
Co-fondateur & CTO
Coming from the tech startup ecosystem, Thibault has developed expertise in AI solution architecture that he now puts at the service of large companies (Atos, BNP Paribas, beta.gouv). He works on two axes: mastering AI deployments (local LLMs, MCP security) and optimizing inference costs (offloading, compression, token management).
Related Articles
Discover more articles on similar topics
Translate Gemma: Multimodal Capabilities in Action
I've been diving into Translate Gemma, and let me tell you, it's a real game changer for multilingual projects. First, I set it up with my existing infrastructure, then explored its multimodal capabilities. With a model supporting 55 languages and training data spanning 500 more, it's not just about language—it's about how you deploy and optimize it for your needs. I'll walk you through how I made it work efficiently, covering model variant comparisons, training processes, and deployment options. Watch out for the model sizes: 4 billion, 12 billion, up to 27 billion parameters—this is heavy-duty stuff. Ready to see how I used it with Kaggle and Hugging Face?
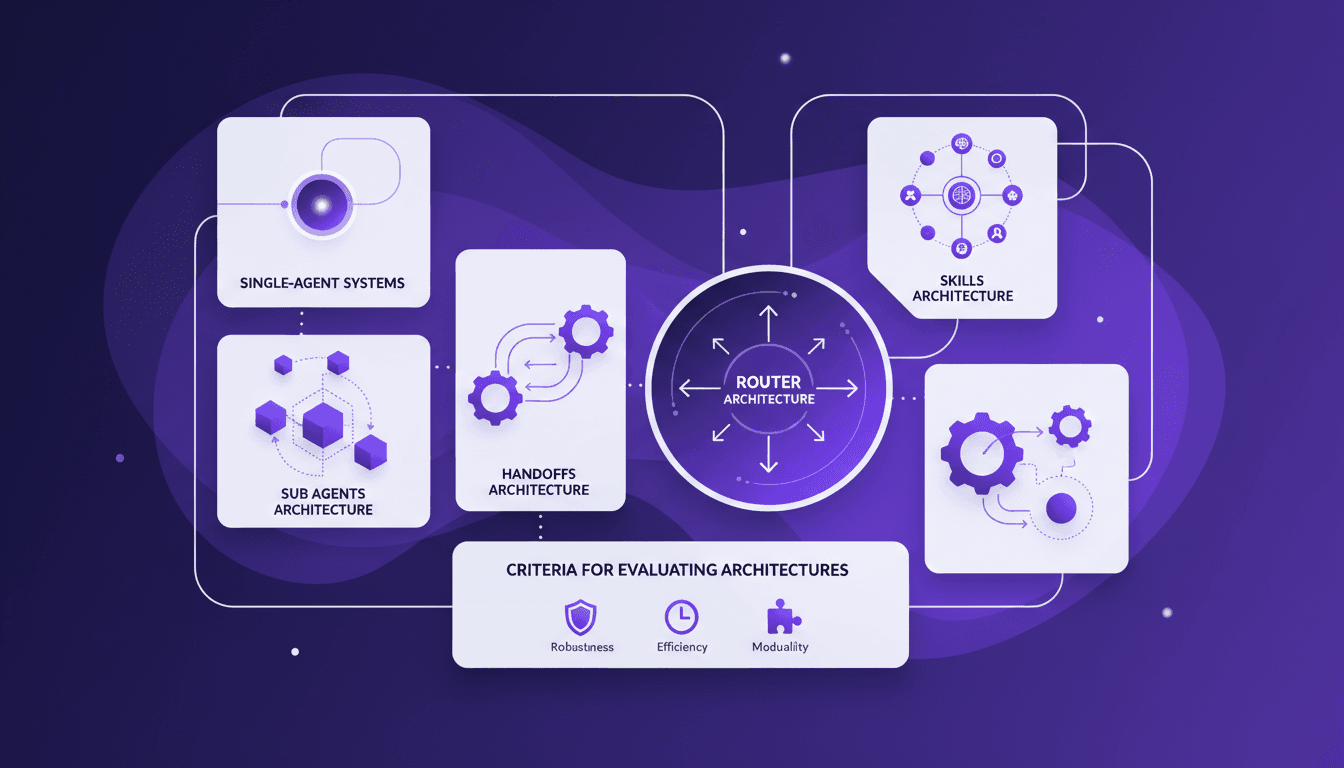
Choosing the Right Multi-Agent Architecture
I remember the first time I tried to implement a multi-agent system. Overwhelmed by the architecture choices, I made a few missteps before finding a workflow that actually works. Here’s how you can choose the right architecture without the headaches. Multi-agent systems can really change how we tackle complex tasks by distributing workload and enhancing interaction. But pick the wrong architecture, and you could face an efficiency and scalability nightmare. We'll explore sub agents, handoffs, skills, and router architectures, plus criteria for evaluating them. And why sometimes, starting with a single-agent system is a smart move. I'll share where I stumbled and where I succeeded to help you avoid the pitfalls. Ready to dive in?
Rapid Adoption of Cloud Code: Why It Changes Everything
I started using Cloud Code back in 2026, and let me tell you, it’s been a game-changer. At first, I was skeptical—another tool promising to revolutionize coding. But then, I saw the command-level interface in action, and things clicked. Cloud Code is quickly becoming the go-to tool for developers. It's not just about writing code; it's about transforming how we approach development. In this article, I'll dive into why so many people are making the switch and how you can harness its power. We’ll cover the rapid adoption of Cloud Code, its unique interface, and how the ecosystem is expanding. Don't miss this if you want to stay ahead of the curve!
Build an AI Business for $1 in 2026
I started my AI business with just a dollar. Sounds crazy? Well, in 2026, thanks to AI tools, it's not only possible but practical. I orchestrated everything using dropshipping platforms, marketing strategies with influencers, and mailing lists. Every dollar counts, especially when it comes to AI and branding. Leveraging free trials and tools like AutoDS, I turned that initial dollar into thousands in monthly sales. Let me show you how I did it, step by step, so you can embark on this journey too.
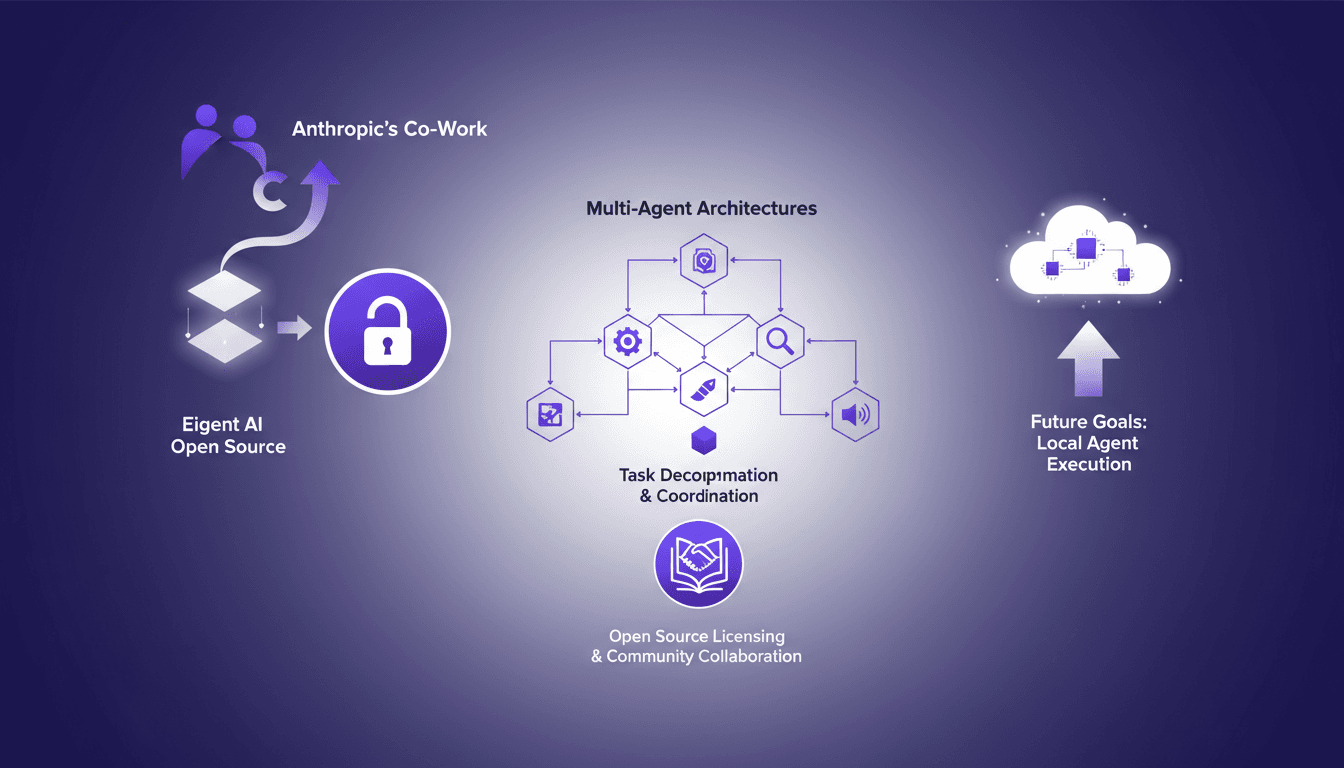
Eigent AI Open Sources to Challenge Claude Cowork
I remember the day Eigent AI decided to open source our product. It was a bold move, inspired by Anthropic's co-work release. This decision reshaped our approach to multi-agent architectures. By opening up our architecture, we aimed to leverage community collaboration and enhance our multi-agent systems. The challenge was significant, but the results were worth it, especially in terms of task decomposition and coordination using DAG. If you're curious about how this has shaken up our development process, let's dive into this transformation together.