Ollama Launch: Tackling Mac Challenges
I remember the first time I fired up Ollama Launch on my Mac. It was like opening a new toolbox, gleaming with tools I was eager to try out. But the real question is how these models actually perform. In this article, we'll dive into Ollama Launch features, put the GLM 4.7 flash model through its paces, and see how Claude Code stacks up. We'll also tackle the challenges of running these models locally on a Mac and discuss potential improvements. If you've ever tried running a 30-billion parameter model with a 64K context length, you know what I'm talking about. So, ready to tackle the challenge?
I vividly remember the first time I fired up Ollama Launch on my Mac. It felt like opening a brand-new toolbox, packed with gleaming tools I couldn't wait to test out. But, as always, the real test is in the execution. First, I dove into the features of Ollama. It didn't take long to hit the default context length limit of Lama at 4,096 tokens. Fine for basic tasks, but when you push it to 64K, you're in a whole new ballgame. Next, I put the GLM 4.7 flash model through its paces. Again, watch out for performance dips if you don't handle context well. As for Claude Code, it holds its own, but remember, it has its limits. And for those like me who love running everything locally on a Mac, it's quite the challenge. But with a few tweaks, especially in orchestration, you can really bump up performance. In the end, it's the small details that make the difference.
Exploring Ollama Launch Features
First off, let's dive into Ollama Launch, a new feature that's made my life much easier for running Claude Code with Anthropic API support. I set it up on my Mac Mini Pro with 32GB of memory (yes, it's quite a beast), and honestly, I was pleasantly surprised by how user-friendly it is. No need for hours of tinkering—everything is practically plug-and-play.

What really stood out to me is the ability to launch models like Claude Code or GLM 4.7 Flash without turning the setup into a nightmare. But watch out—if you don't set the context length right, things can quickly go south.
Putting the GLM 4.7 Flash Model to the Test
Next, let's talk about testing the GLM 4.7 Flash model, which is a compact version of the GLM 4.7 with 30 billion parameters, out of which three billion are active. I configured a 64K context length for this model, which is crucial for its performance. Don't be fooled by the high parameter count—it's not always synonymous with better performance.
After 90 minutes of testing, I realized that quantization plays a huge role here. Sometimes quantization reduces precision but also speeds up execution. It's a trade-off between accuracy and speed that needs careful consideration.
- 30 billion parameters, but only three billion active.
- 64K context for optimized performance.
- Be wary of the trade-offs between quantization and precision.
The Importance of Context Length
Context length is like the short-term memory of a model. By default, Lama uses a length of 4,096. To get better results, I tweaked it to 64K. What a difference! But beware, pushing the context length too far can saturate memory and slow down processing.
By adjusting this variable, I was able to significantly improve performance, but always be mindful of hardware limitations.
Running Models Locally on a Mac: Challenges and Solutions
Running these models locally is quite a challenge. Even with 32GB RAM on my Mac Mini Pro, juggling memory management is key. Claude Code, for instance, can become painfully slow if you're not careful. I had to employ tricks to optimize local execution, like managing background processes and resource optimization.
Future improvements could make local execution more viable, but for now, it's limited without a powerful GPU.
Claude Code vs. Other Models: A Performance Review
Finally, let's compare Claude Code to the GLM 4.7 model. With the Anthropic API, Claude Code has its strengths but also some weaknesses. I noted efficiency gains, but there are areas where Claude Code could improve, particularly in execution speed and resource management.
Future developments could bridge these gaps, but for now, Claude Code shines mainly due to its flexibility and integration with other tools.
- Claude Code performs well thanks to the Anthropic API.
- Needs improvements in speed and resource management.
- Promising future with ongoing developments.
After diving into Ollama Launch and testing GLM 4.7 and Claude Code, these tools show exciting potential, but be prepared for some challenges. First, optimizing context length is key. Shifting to a 64K context length instead of the default 4,096 of Lama was a game changer. Next, running these models locally on a Mac isn’t without its hiccups. With a 30 billion parameter model and 3 billion active, local performance demands careful tweaking. Finally, it's all about balancing the technological potential with hardware constraints.
Looking ahead, optimizing local execution and context lengths is truly the lever to unlock these tools' full potential. Ready to take your model execution to the next level? Start experimenting and share your findings with the community. For a deeper dive, watch the original video — it's a great starting point for this adventure.
Frequently Asked Questions

Thibault Le Balier
Co-fondateur & CTO
Coming from the tech startup ecosystem, Thibault has developed expertise in AI solution architecture that he now puts at the service of large companies (Atos, BNP Paribas, beta.gouv). He works on two axes: mastering AI deployments (local LLMs, MCP security) and optimizing inference costs (offloading, compression, token management).
Related Articles
Discover more articles on similar topics
Clone Any Voice for Free: Qwen TTS Revolutionizes
I remember the first time I cloned a voice with Qwen TTS—it was like stepping into the future. Imagine having such a powerful tool, and it's open source, right at your fingertips. This isn't just theory; it's about real-world application today. Last June, Qwen announced their TTS models, and by September, the Quen 3 TTS Flash with multilingual support was ready. For anyone interested in voice cloning and multilingual speech generation, this is a true game changer. With models ranging from 0.6 billion to 1.7 billion parameters, the possibilities are vast. But watch out, there are technical limits to be mindful of. In this article, I'll guide you through multilingual capabilities, open-source release, and emotion synthesis. Get ready to explore how you can leverage this tech today.
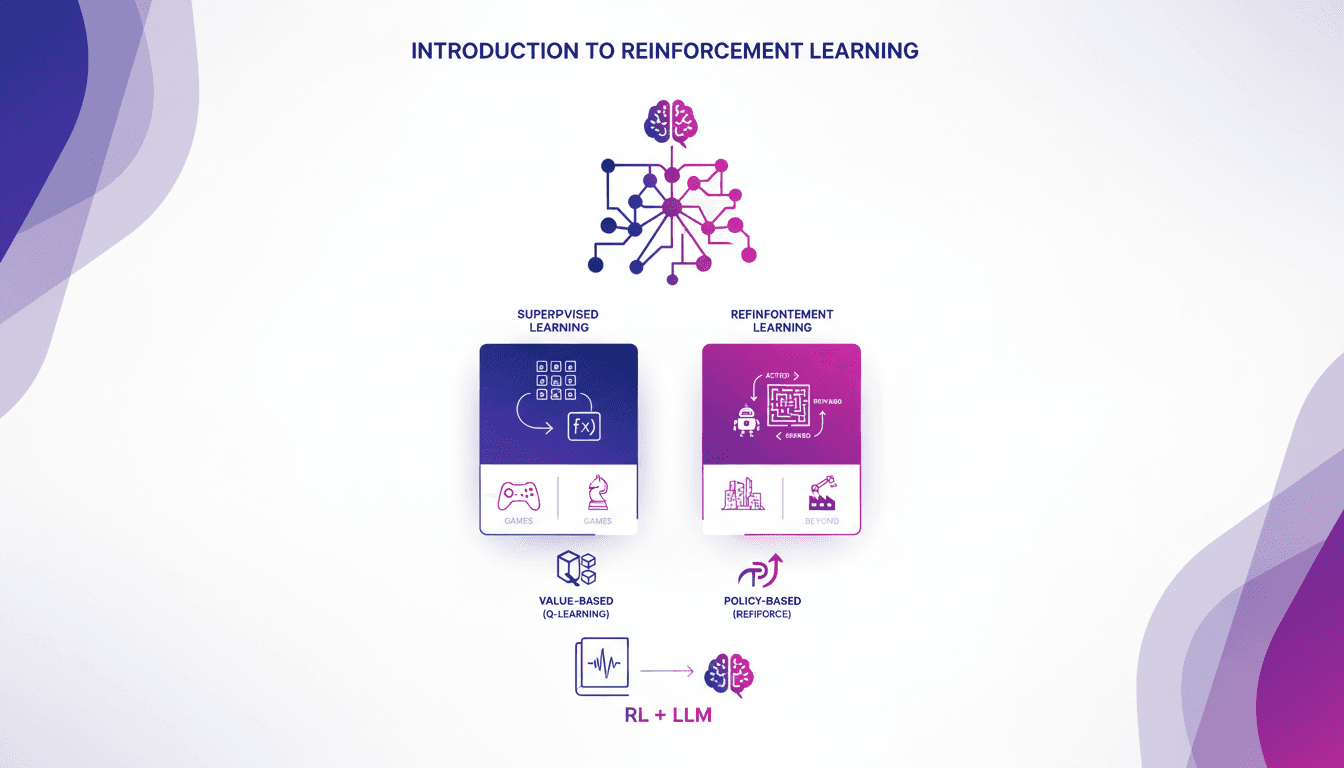
Practical Intro to Reinforcement Learning
I remember the first time I stumbled upon reinforcement learning. It felt like unlocking a new level in a game, where algorithms learn by trial and error, just like us. Unlike supervised learning, RL doesn't rely on labeled datasets. It learns from the consequences of its actions. First, I'll compare RL to supervised learning, then dive into its real-world applications, especially in games. I'll walk you through value-based methods like Q-learning and policy-based methods, showing how these approaches are transforming massive language models. In the end, you'll see how three key ways of using RL to fine-tune large language models deliver impressive results.
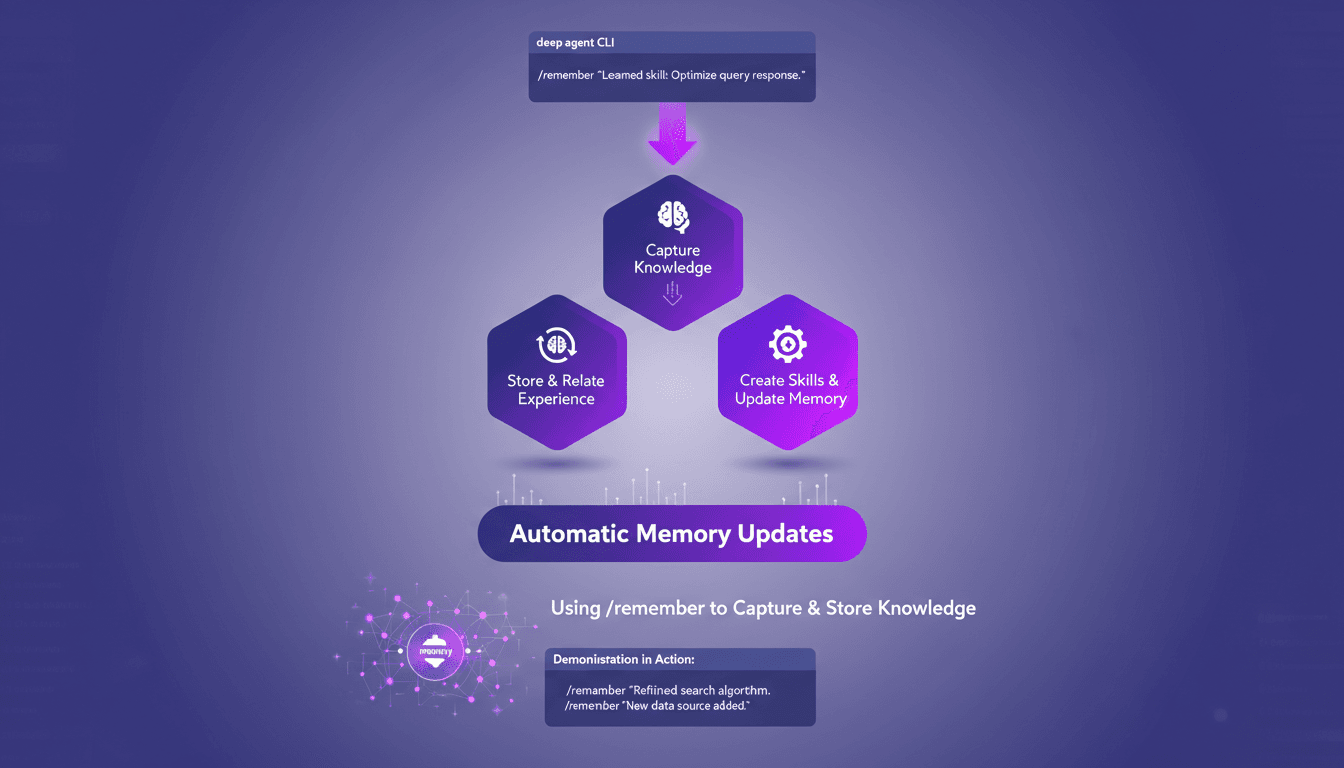
Mastering /remember: Deep Agent Memory in Action
I've spent countless hours tweaking deep agent setups, and let me tell you, the /remember command is a game changer. It's like giving your agent a brain that actually retains useful information. Let me show you how I use it to streamline processes and boost efficiency. With the /remember command in the deep agent CLI, you can teach agents to learn from experience. Let's dive into how this works and why it's a must-have in your toolkit.
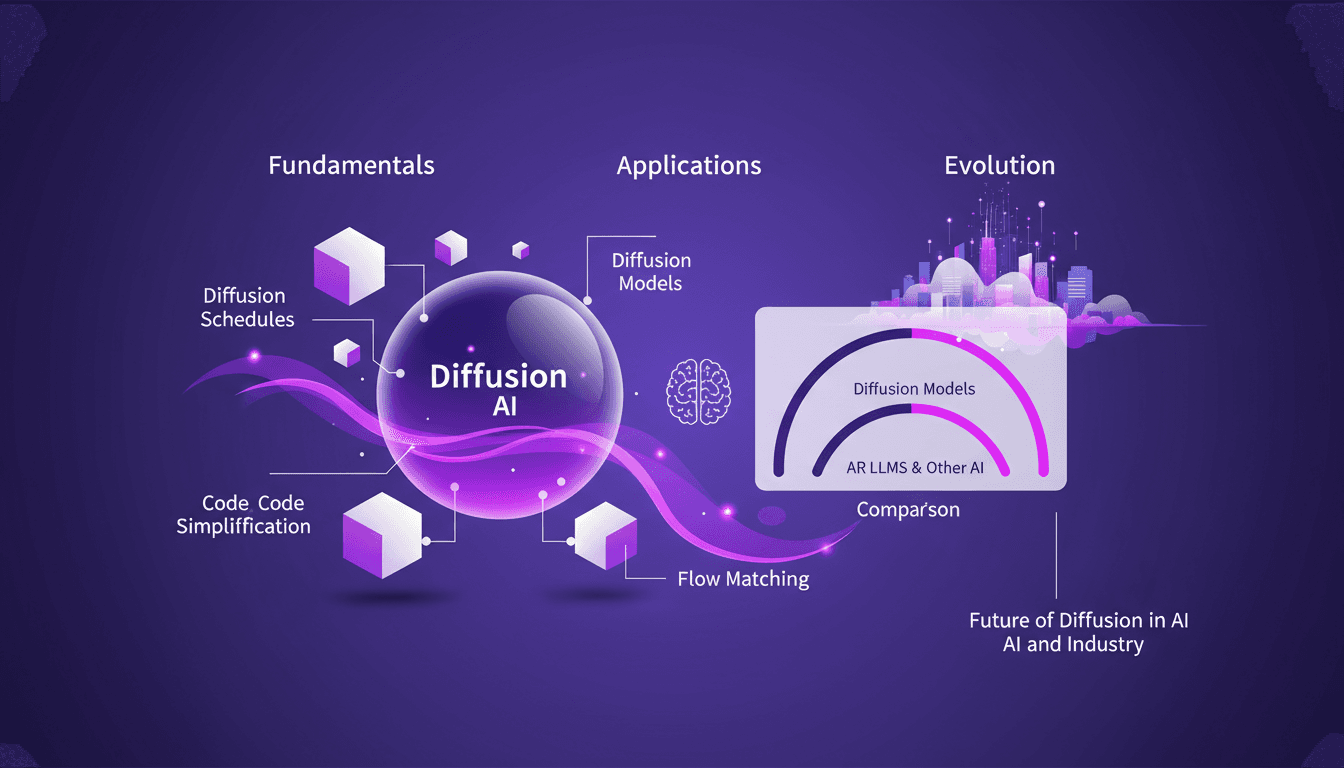
Mastering Diffusion in ML: A Practical Guide
I've been knee-deep in machine learning since 2012, and let me tell you, diffusion models are a game changer. And they're not just for academics—I'm talking about real-world applications that can transform your workflow. Diffusion in ML isn't just a buzzword. It's a fundamental framework reshaping how we approach AI, from image processing to complex data modeling. If you're a founder or a practitioner, understanding and applying these techniques can save you time and boost efficiency. With just 15 lines of code, you can set up a powerful machine learning procedure. If you're ready to explore AI's future, now's the time to dive into mastering diffusion.
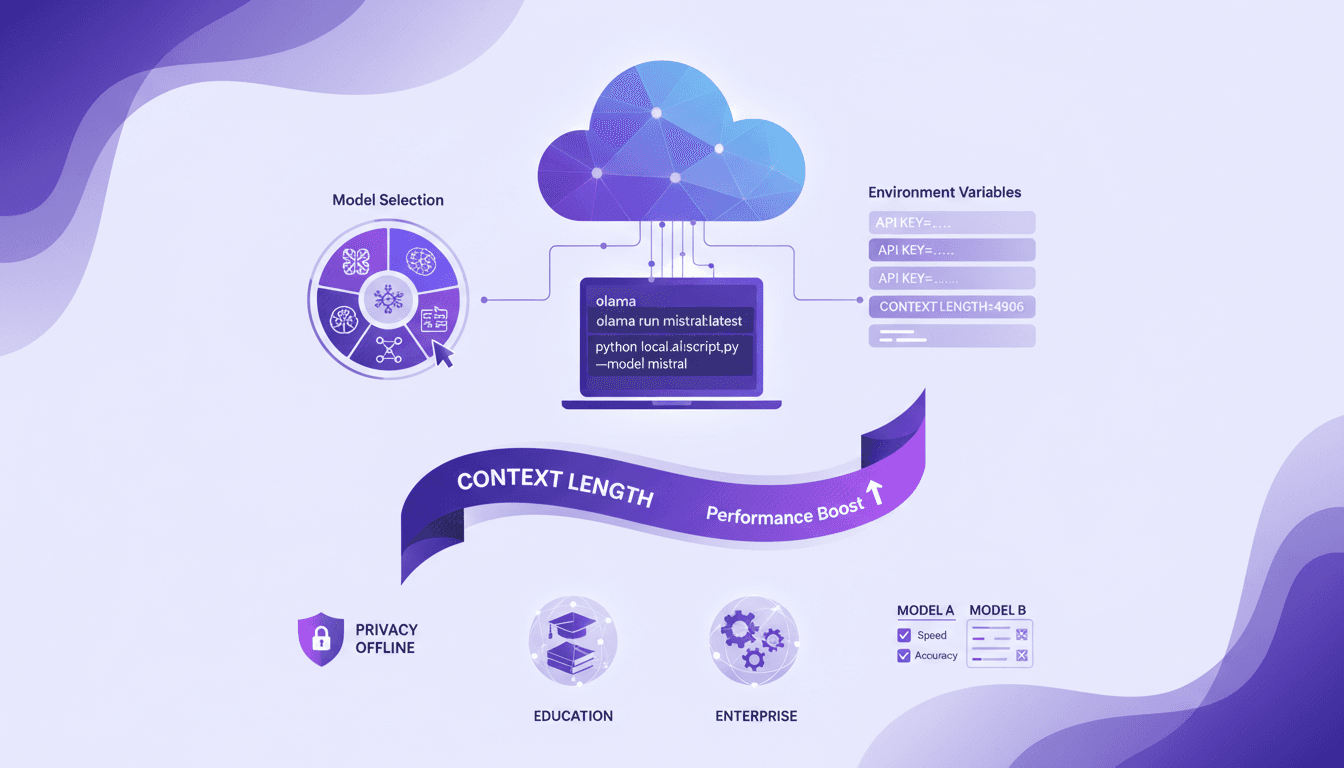
Run Cloud Code Locally with Olama: Tutorial
I've been running cloud code locally to boost efficiency and privacy, and Olama has been a real game changer. Imagine handling AI models with 4 billion parameters, all without leaving your desk. I'll show you how I set it up, from model selection to tweaking environment variables, and why it’s a game changer for education and enterprise. But watch out for context limits: beyond 100K tokens, things get tricky. By using Olama, we can compare different AI models for local use while ensuring enhanced privacy and offline capabilities. The goal here is to give you a practical, hands-on look at how I orchestrate these technologies in my professional life.