Llama 4 Deployment and Open Source Challenges
I dove headfirst into the world of AI with Llama 4, eager to harness its power while navigating the sometimes murky waters of open source. So, after four intensive days, what did I learn? First, Llama 4 is making waves in AI development, but its classification sparks heated debates. Is it truly open-source, or are we playing with semantics? I connected the dots between Llama 4 and the concept of open-source AI, exploring how these worlds intersect and sometimes clash. As a practitioner, I take you into the trenches of this tech revolution, where every line of code matters, and every technical choice has its consequences. It's time to demystify the terminology: open model versus open-source. But watch out, there are limits not to cross, and mistakes to avoid. Let's dive in!
I recently dove into the world of Llama 4, and let me tell you, it's a real challenge to navigate between the power of this tool and the complexities of open source. From the get-go, I realized that Llama 4 isn't just another player in AI development; it's a storm raising questions about its classification. Open-source or not? That's the burning question on everyone's mind. As a practitioner, I found myself sifting through the promises and the reality. I connected my development environment, orchestrated deployments, and sometimes, I got burned by technical limitations. It's a universe where every technical choice can have a direct impact on efficiency and costs. And then there's this terminology issue: open model versus open-source, a distinction that's not always crystal clear. But beware, there are pitfalls to avoid, and I learned the hard way that you can't take everything at face value. Join me as we dive into what's behind Llama 4 and the future of open-source AI models.
Understanding Llama 4 and Its Role
When I first heard about Llama 4, it was clear that integrating it into my workflow was crucial to stay ahead. This AI model is touted as a game changer, and frankly, it lives up to the hype. I started by setting up the environment, connecting my repos to the official Llama API. However, the initial steps weren't straightforward. Navigating through the multilingual token configurations was tricky — Llama 4 is pre-trained on over 200 languages, which is impressive but complex to manage. I had to tweak my settings multiple times before hitting the sweet spot. Why all the buzz around Llama 4? Because it marks a significant step toward an open-source AI model, a leap many in the field have been waiting for.

The Open-Source AI Landscape
Let's talk about open-source AI. As a practitioner, I see it as a double-edged sword. On one hand, open-source offers transparency and collaboration that are essential for innovation. On the other hand, it can be a nightmare in terms of management and integration. In my projects, I've often leveraged open-source models to cut costs — and it works! In fact, a 2024 GitHub report showed a 98% increase in contributions to open-source projects, highlighting the real impact on efficiency. However, you need to be cautious about license compatibility and the legal implications of open-source models.
Classifying Llama 4: Open Source or Not?
The burning question: Is Llama 4 truly open-source? There's debate. Some call it an open model, while others prefer the term open weight model. In my experience, using it under this classification comes with trade-offs. For example, licensing restrictions can limit your ability to modify and redistribute the model. I've seen projects fail because they didn't correctly assess these constraints. Llama 4, while impressive, isn't the ideal open-source solution for everyone. You need to fully understand the implications before diving in.
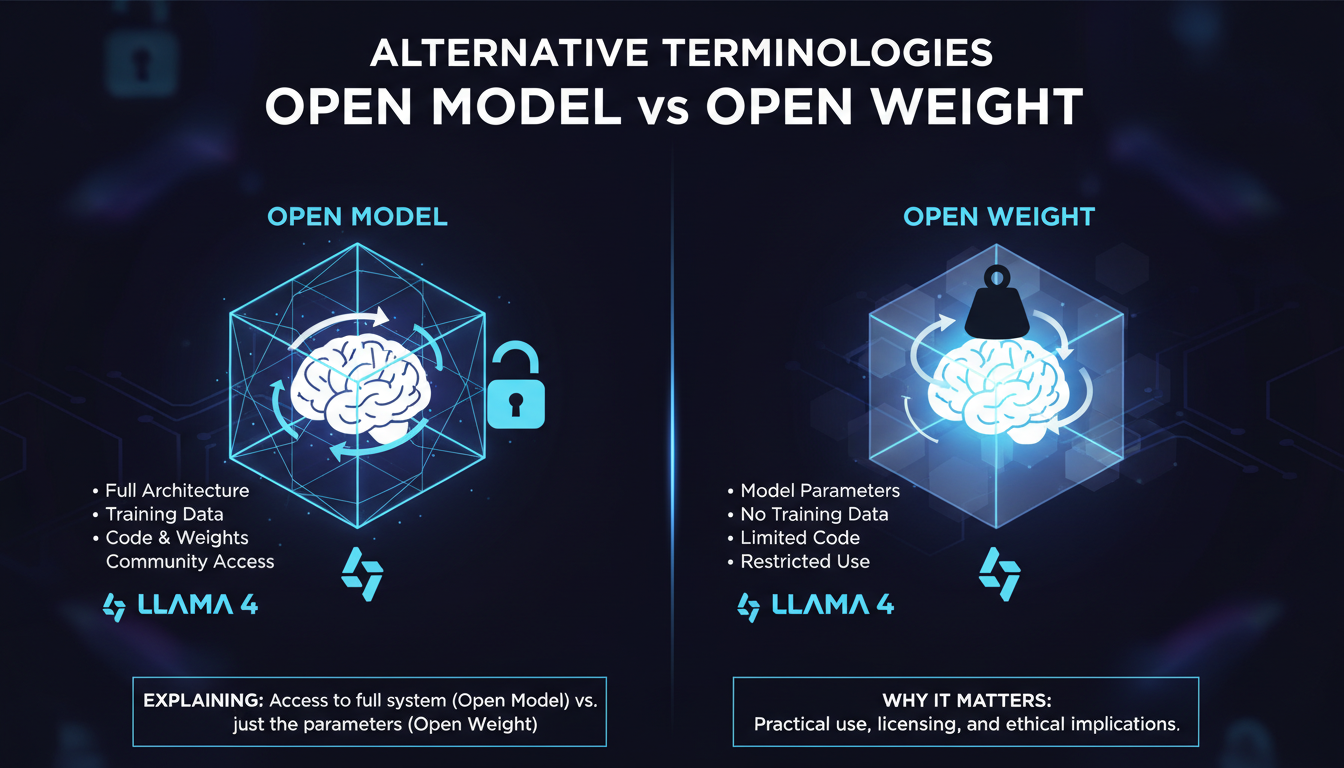
Alternative Terminologies: Open Model vs Open Weight
When discussing Llama 4, the terms 'open model' and 'open weight' frequently come up. But what do they really mean? Essentially, an open model implies that the source code is accessible for modifications, whereas an open weight refers to the availability of the model weights for adjustments. Why does it matter? Because it directly affects how you can use and adapt the model to your needs. I've seen teams waste time simply because they didn't understand these distinctions. In a practical setting, understanding these terms can mean the difference between a successful project and a spectacular flop.
The Future of Open-Source AI Models
Looking ahead, I'm convinced that open-source AI models will dominate the industry. But there's a delicate balance to maintain between innovation and open-source principles. With Llama 4, I've learned you can't have it all: flexibility, accessibility, and performance. You have to choose your battles. However, the lessons learned from its implementation are invaluable. I anticipate models like Llama 4 will continue to influence how we approach AI integration in our products. Until then, staying vigilant to evolutions and always seeking optimization is key.
So, Llama 4 is like the Swiss Army knife for AI developers navigating the open-source debate. First, understanding how Llama 4 is classified helps avoid deployment pitfalls. Then, Llama 4 shows us that open-source can really speed up innovation, but watch out for classification limits that can hinder adoption. It's a real game changer, but let's not kid ourselves: every advantage has its downside. Open-source models come with hidden costs in terms of maintenance and security. Looking ahead, I'd say we have a lot more to explore with these models. The insights we gain from these tools can truly boost our AI projects. I highly recommend diving into your own AI projects with these lessons in mind. Watch the full video to deepen your understanding—it's really practical stuff for those of us who build every day.
Frequently Asked Questions

Thibault Le Balier
Co-fondateur & CTO
Coming from the tech startup ecosystem, Thibault has developed expertise in AI solution architecture that he now puts at the service of large companies (Atos, BNP Paribas, beta.gouv). He works on two axes: mastering AI deployments (local LLMs, MCP security) and optimizing inference costs (offloading, compression, token management).
Related Articles
Discover more articles on similar topics
Nvidia AI Supercomputer: Power and Applications
I plugged in Nvidia's new personal AI supercomputer, and let me tell you, it's like trading in your bicycle for a jet. We're talking about a device that outpaces your average laptop by a thousand times. This gem can handle 200 billion parameter models, thanks to the gb10 Grace Blackwell chip. But watch out, this colossal power brings its own challenges. It's a real game changer for individual users, but you need to know where to set the limits to avoid getting burned. Let's dive into what makes this tool exceptional and where you might hit a wall.
Manus AI: Reinventing Automation and Creativity
I dove into Manus AI, expecting just another tool, but it turned my workflow upside down. From coding games to planning trips, this AI agent is a real game changer. Developed by Meta GPT, it offers zero-shot task completion that cuts through the hype. I'm here to show you how I've integrated it into my daily projects. But watch out, you need to know its limits and orchestrate it effectively. And then there's Open Manis, the open-source alternative, which has already garnered 8,000 stars on its repo. Ready to discover what Manus can really do?
StepFun AI Models: Efficiency and Future Impact
I dove into StepFun AI's ecosystem, curious about its text-to-video capabilities. Navigating through its models and performance metrics, I uncovered a bold contender from China. With 30 billion parameters and the ability to generate up to 200 frames per second, StepFun AI promises to shake up the AI landscape. But watch out, the Step video t2v model demands 80 GB of GPU memory. Compared to other models, there are trade-offs to consider, yet its potential is undeniable. Let's explore what makes StepFun AI tick and how it might redefine the industry.
Why We Donated MCP to Linux
I was knee-deep in code when the idea hit me—what if we made the Model Context Protocol open-source? It wasn't just about sharing; it was about community and innovation. Donating the MCP to the Linux Foundation was our way of pushing boundaries and inviting others to join the journey. The technical challenges were many: security, context bloat, but that’s what makes the project exciting. The Agentic AI Foundation plays a crucial role in MCP's adoption and impact within the AI community. Our decision wasn't just a donation; it was an invitation to innovate together. Now, let's dive into the details.
Claude: Philosophy and Ethics in AI
I joined Anthropic not just as a philosopher, but as a builder of ethical AI. First, I had to grasp the character of Claude, the AI model I’d be shaping. This journey isn't just about coding—it's about embedding ethical nuance into AI decision-making. In the rapidly evolving world of AI, ensuring that models like Claude make ethically sound decisions is crucial. This isn't theoretical; it's about practical applications of philosophy in AI. We tackle the character of Claude, nuanced questions about AI behavior, and how to teach AI ethical behavior. As practitioners, I share with you the challenges and aspirations of AI ethics.