Building a Real-Time AI Agent with Cerebras
I remember the first time I connected a Cerebras system to my AI workflow. The speed was jaw-dropping, but it quickly became clear it wasn't just about speed. It's about orchestrating everything efficiently, from speculative decoding to real-time voice data transfer. With Cerebras's Wafer Scale Engine 3, we're pushing the boundaries of AI inference and real-time applications. In this article, I'll take you through the process of building a real-time AI sales agent using Cerebras hardware, including a comparison with Nvidia GPUs. We'll explore how speculative decoding and Live Kit technology are revolutionizing user experience. Buckle up, because we'll also dive into training AI sales agents with LLMs and expanding into multi-agent systems for specialized support. Let's get started!
I still remember the first time I connected a Cerebras system to my AI workflow. The speed was jaw-dropping, but hold on, it's not just about speed. It's about orchestrating every piece efficiently. First, I had to grasp speculative decoding—key for fast inference—then I integrated real-time voice data transfer. With Cerebras's Wafer Scale Engine 3, packing 4 trillion transistors and 900,000 cores, we are stepping into a new era of AI. This isn't just theory; it's hands-on: building smarter, faster AI systems that can revolutionize our business practices. In this article, I'll show you how I built a real-time AI sales agent. We'll also compare it with Nvidia GPUs and discuss how speculative decoding and Live Kit technology are reshaping user experience. Plus, we'll cover training AI sales agents with LLMs and expanding into multi-agent systems for specialized support. Ready to push the boundaries? Let's dive in!
Understanding Cerebras Hardware Innovations
When it comes to computational power, Cerebras sets the bar high with its Wafer Scale Engine 3. Imagine a chip the size of a dinner plate, packed with 4 trillion transistors and 900,000 cores. It's a beast. Compared to Nvidia GPUs, it's like David versus Goliath, except this time, David has a significant lead. In terms of inference performance, Cerebras outpaces its competitors by 20 to 70 times. Why? Thanks to an architecture that eliminates memory bandwidth bottlenecks. No constant data shuffling between cores and external memory, everything is within reach on the chip.
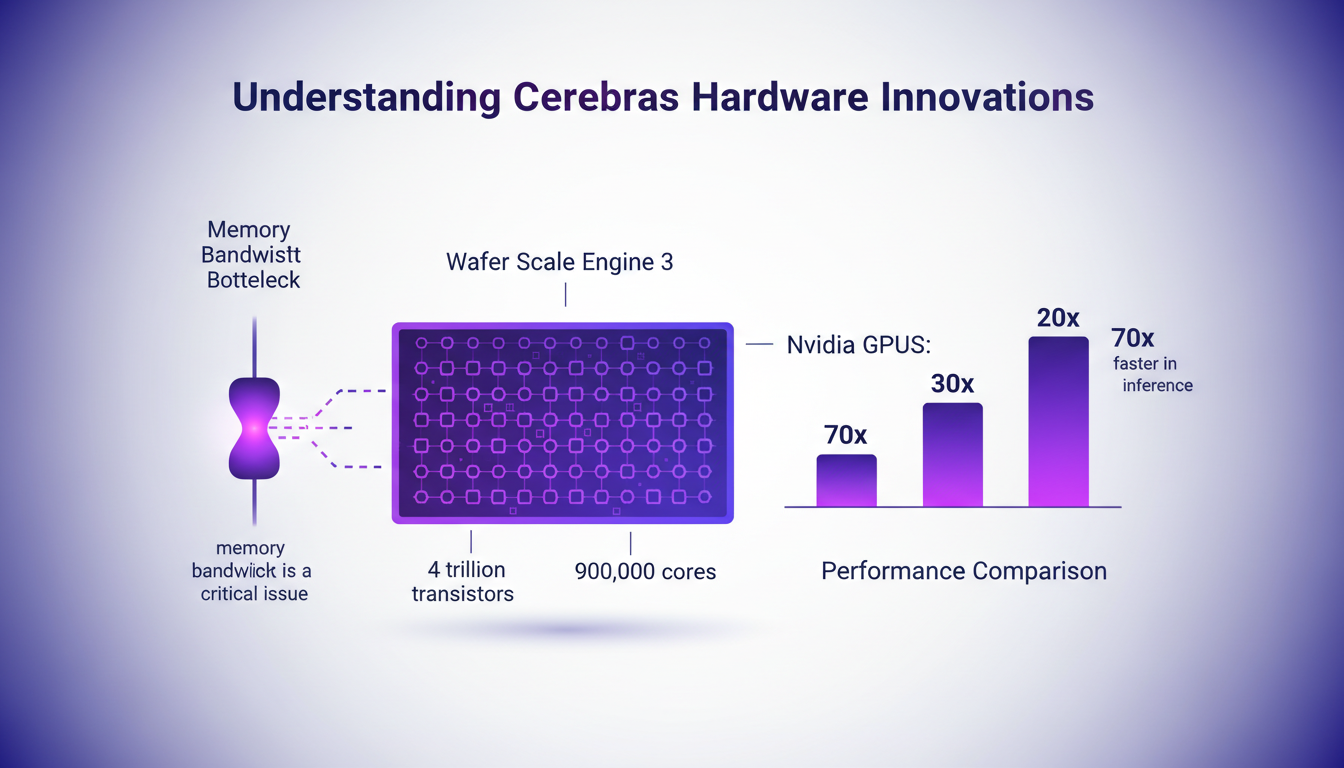
"Cerebras solved the memory bottleneck issue, a real hurdle for traditional GPUs."
For AI developers, this is a boon. No more juggling with hardware limitations. We can focus on optimizing the algorithm, not the hardware. It's a considerable time and energy saver.
Building a Real-Time AI Voice Agent
Integrating Cerebras into an AI voice system is like upgrading from a bicycle to a race car. First, I connect Cerebras to my AI system. Then, I use speculative decoding to boost inference speed. It's not just about speed; it's also about adaptability. A good voice agent must be accurate, fast, and capable of adapting to real-time demands.
The challenges are numerous: from compatibility issues to algorithm adjustments. But once these hurdles are overcome, the impact is direct. An agent that understands and responds smoothly is a major asset.
Speculative Decoding: Speeding Up Inference
Speculative decoding is like anticipating the needs of your race car. We predict possible outcomes and test them in parallel. It saves time, but you need to balance speed with accuracy. Too much speed, and you risk errors. Too much accuracy, and you lose the speed advantage.
I've seen systems crash because they bet everything on speed. So, how to avoid this? By finely tuning the algorithm and monitoring real-time results. It takes time, but the efficiency gains are undeniable.
"The impact on real-time applications is huge, but beware of the pitfalls of excessive speed."
Leveraging Live Kit for Low-Latency Voice Data
With Live Kit, I transmit voice data in real-time using the WebRTC protocol. It's essential to keep latency low and ensure smooth communication. Voice activity detection plays a crucial role. It helps identify when the user is speaking and adjusts processing accordingly.

Orchestrating a multi-agent system is like conducting an orchestra. Each agent has its role, and you need to ensure they all work in harmony. But watch out, too much latency, and it's chaos. Sometimes, you have to sacrifice a bit of quality to maintain fluidity.
Training and Expanding AI Sales Agents
To train AI sales agents, I use LLMs (large language models). It starts with precise training and tool calling to expand their capabilities. But watch out, managing system resources is crucial. Allocate too many resources, and the system collapses.
Anticipating the future means ensuring the system is flexible and can evolve with the market. This is where field experience is invaluable. Each adjustment is a lesson learned and an improvement for the future.
"Training an AI agent is about preparing for the future while optimizing the present."
In summary, Cerebras' innovation, the integration of advanced voice systems, and the use of techniques like speculative decoding transform the way we approach AI today. With the right tools and a pragmatic approach, we can truly revolutionize the sector.
Building real-time AI systems with Cerebras is a game changer, but let's not ignore the challenges. First, I got my hands dirty with speculative decoding to push inference speed. Then, I tackled low-latency data transfer—it's crucial for performance. By orchestrating all these elements smartly, I can create AI agents that not only meet today's demands but are ready for tomorrow's challenges.
- 4: Four key capabilities of voice agents to harness.
- 4 trillion: Transistors in the Wafer Scale Engine 3.
- 900,000: Cores in the Wafer Scale Engine 3.
The future is looking bright: by integrating Cerebras hardware into our workflows, we can truly revolutionize our AI systems. Ready to transform your AI systems? Start with Cerebras today. For deeper insights, I highly recommend watching the full video: YouTube link.
Frequently Asked Questions

Thibault Le Balier
Co-fondateur & CTO
Coming from the tech startup ecosystem, Thibault has developed expertise in AI solution architecture that he now puts at the service of large companies (Atos, BNP Paribas, beta.gouv). He works on two axes: mastering AI deployments (local LLMs, MCP security) and optimizing inference costs (offloading, compression, token management).
Related Articles
Discover more articles on similar topics
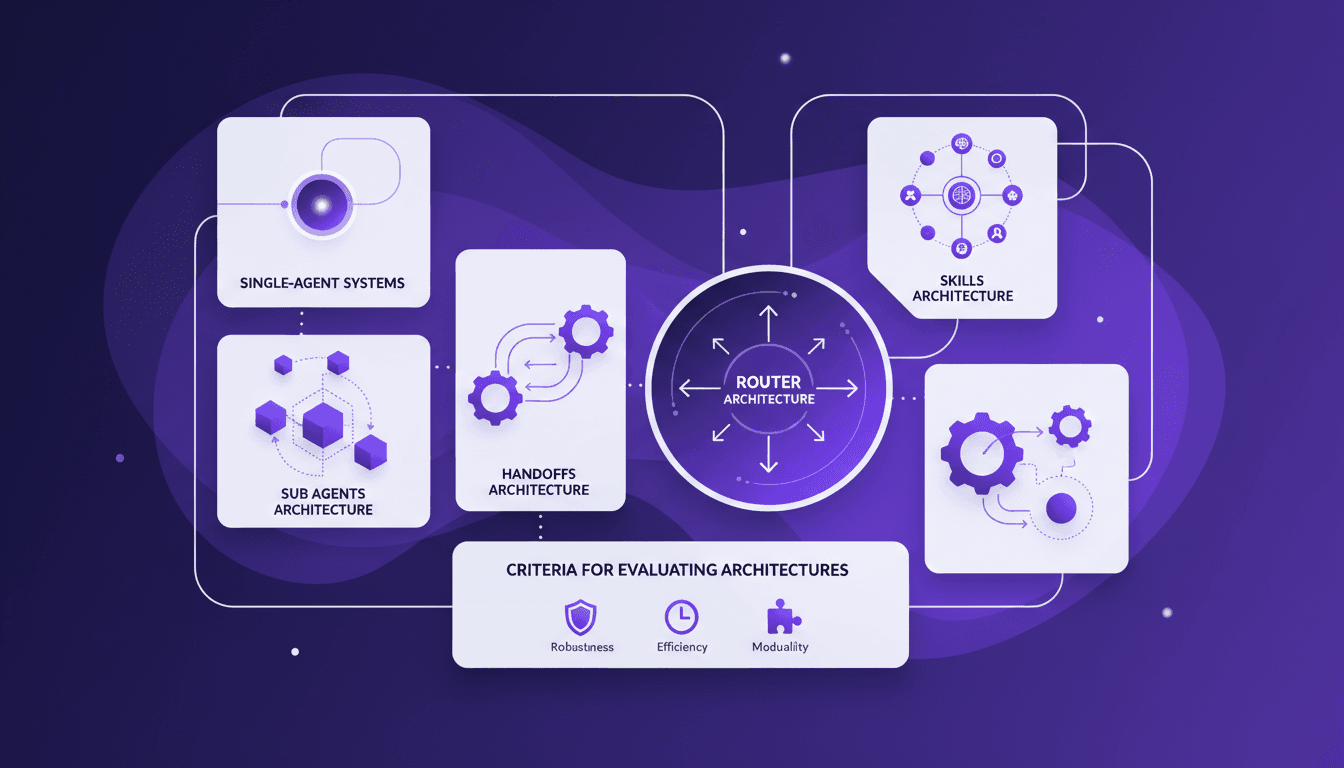
Choosing the Right Multi-Agent Architecture
I remember the first time I tried to implement a multi-agent system. Overwhelmed by the architecture choices, I made a few missteps before finding a workflow that actually works. Here’s how you can choose the right architecture without the headaches. Multi-agent systems can really change how we tackle complex tasks by distributing workload and enhancing interaction. But pick the wrong architecture, and you could face an efficiency and scalability nightmare. We'll explore sub agents, handoffs, skills, and router architectures, plus criteria for evaluating them. And why sometimes, starting with a single-agent system is a smart move. I'll share where I stumbled and where I succeeded to help you avoid the pitfalls. Ready to dive in?
Caterpillar's AI Integration: 100 Years of Innovation
I remember the first time I saw a Caterpillar machine in action—it was a game changer in construction. Fast forward to CES 2026, and we're now discussing AI-driven innovations that could redefine the entire industry. As Caterpillar celebrates its centennial, they're pushing boundaries with machine learning, in partnership with Nvidia. We're not just talking about autonomous systems in mining and construction, but a whole ecosystem of autonomy and connectivity. And watch out, with the introduction of their CAT AI Assistant, there's a clear promise to transform how we approach workforce development and the future of autonomy in this sector. No empty promises here, just concrete solutions aiming to make a real impact.
Translate Gemma: Multimodal Capabilities in Action
I've been diving into Translate Gemma, and let me tell you, it's a real game changer for multilingual projects. First, I set it up with my existing infrastructure, then explored its multimodal capabilities. With a model supporting 55 languages and training data spanning 500 more, it's not just about language—it's about how you deploy and optimize it for your needs. I'll walk you through how I made it work efficiently, covering model variant comparisons, training processes, and deployment options. Watch out for the model sizes: 4 billion, 12 billion, up to 27 billion parameters—this is heavy-duty stuff. Ready to see how I used it with Kaggle and Hugging Face?
Enhance Agent UX: Stream Events with LangChain
I remember the first time I faced lagging user interfaces while working with agent tools. It was frustrating, especially when you're trying to impress a client with real-time data processing. That's when I started integrating custom stream events with LangChain. In this article, I'll walk you through setting up a responsive user interface using LangChain, React, and Typescript. We'll dive into custom stream events, the config.writer function, and deploying with the langraph dev server. If you've ever lost time to sluggish tool calls, this tutorial is for you.
Harnessing Quen 3 Multimodal Embeddings
I dove into Qwen 3's multimodal embeddings, aiming to streamline my AI projects. The promise? Enhanced precision and efficiency across over 30 languages. First, I connected the embedding models, then orchestrated the rerankers for more efficient searches. The results? A model reaching 85% precision, a real game changer. But watch out, every tool has its limits and Qwen 3 is no exception. Let me walk you through how I set it up and the real-world impact it had.