LLMs Optimization: RLVR and OpenAI's API
I've been knee-deep in fine-tuning large language models (LLMs) using Reinforcement Learning via Verifiable Rewards (RLVR). This isn't just theory; it's a game of efficiency and cost, with OpenAI’s RFT API as my main tool. In this tutorial, I'll walk you through how I make it work. We're diving into the training process, tackling imbalanced data, and comparing fine-tuning methods, all while keeping a close eye on costs. This is our third episode on reinforcement learning with LLMs, and we'll also discuss OpenAI's RFT API alternatives. Quick heads up: at $100 per hour, it escalates fast!
When I first dove into fine-tuning massive language models (LLMs) using Reinforcement Learning via Verifiable Rewards (RLVR), I wasn't ready for the challenge. It's not just theory; it's a game of efficiency and cost, especially with OpenAI’s RFT API. Let me take you behind the scenes of my workflow: it starts with data prep (often imbalanced, which complicates things), then comparing supervised and reinforcement fine-tuning methods. Watch out for the pitfalls because at $100 an hour, mistakes are pricey. In this third video of our series, I'll also show you some alternatives to OpenAI's API. It's a real journey, but once you know where to look and how to tweak, the results can be spectacular. Join me, and I'll show you how I do it.
Understanding RLVR in LLMs
Let's cut to the chase: when we talk about reinforcement learning (RL), we're talking about adaptive decision-making. Large Language Models (LLMs) thrive on this concept, improving through trial and error. The new kid on the block is Reinforcement Learning via Verifiable Rewards (RLVR). Instead of relying solely on human feedback or approximations, RLVR uses verifiable rewards to steer LLMs towards tangible outcomes.
"RLVR doesn't just train the model to generate good responses, but to achieve outcomes."
Why does this matter? Because it structures outputs in a consistent way. This enhances the adaptive reasoning processes of LLMs. But watch out, too much RLVR can lead to overfitting. I've seen models become too rigid, losing the flexibility that makes them effective.
Training Process: Data Prep and Formatting
When kicking off a training project, the first step is always data splitting. We start with a five-step methodical approach. First, 80% of the data goes to normal examples and 20% to anomalies. This balance is crucial for optimal RLVR performance. Next up is data formatting.
Validation is another critical point. After resampling, I always ensure there are at least 50 validation examples. Here’s where many stumble: we want precision, but it requires time. Balancing time investment and accuracy is a real juggling act.
Tackling Imbalanced Data and Anomalies
Imbalanced data is the bane of ML specialists. I've often faced datasets where anomalies were rare (2% in some cases). To tackle this, I use resampling techniques. This gives the model more chances to learn. However, this can affect RLVR effectiveness.
Preventing false positives is crucial; otherwise, the model cries wolf too often. A calculated and measured approach is necessary, as I've frequently observed in my projects.
Cost and Efficiency in Reinforcement Fine-Tuning
Cost considerations are unavoidable: $100 an hour for reinforcement fine-tuning API can add up quickly. To minimize this, I've adopted certain efficiency strategies. Comparing supervised to reinforcement fine-tuning is crucial to understanding where and how to save.
Sometimes, it's smarter to use alternatives like TRL or Unsloth to OpenAI's APIs, even if it means some compromises in terms of support and technical limitations. But the cost savings can be substantial.
Exploring Open-Source Alternatives
Open-source alternatives often bring a breath of fresh air. Compared to OpenAI's API, they allow better integration into existing workflows. But be warned, support is less present, and technical challenges are more numerous.
In summary, it's about striking the right balance between cost, performance, and technical support. Integrating these solutions into your workflows requires adjustment, but the benefits can be significant.
- RLVR structures LLM outputs.
- Data formatting and validation are critical.
- Resampling to handle rare anomalies.
- High cost of reinforcement tuning, hence the interest in open-source solutions.
So, diving into fine-tuning LLMs with RLVR, here's what stood out for me. Balancing cost, efficiency, and performance is an art (we're talking $100 per hour for the fine-tuning API, so you'd better get your data prep right from the get-go). Anomaly detection is crucial, and having 50 validation examples post-resampling saved my neck more than once. And don't underestimate the power of choosing the right tools, whether it's OpenAI or open-source alternatives.
Looking ahead, RLVR has the potential to be a game changer for those ready to explore and refine. But watch out for imbalanced data throwing a wrench in the process.
Ready to dive into RLVR for your LLMs? I recommend you start experimenting with OpenAI's RFT API. And if you really want to get to grips with the nitty-gritty, watch the full video here: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=k-94oCJ_WJo. It's the third video in a series on reinforcement learning, and trust me, it's packed with concrete insights.
Frequently Asked Questions

Thibault Le Balier
Co-fondateur & CTO
Coming from the tech startup ecosystem, Thibault has developed expertise in AI solution architecture that he now puts at the service of large companies (Atos, BNP Paribas, beta.gouv). He works on two axes: mastering AI deployments (local LLMs, MCP security) and optimizing inference costs (offloading, compression, token management).
Related Articles
Discover more articles on similar topics
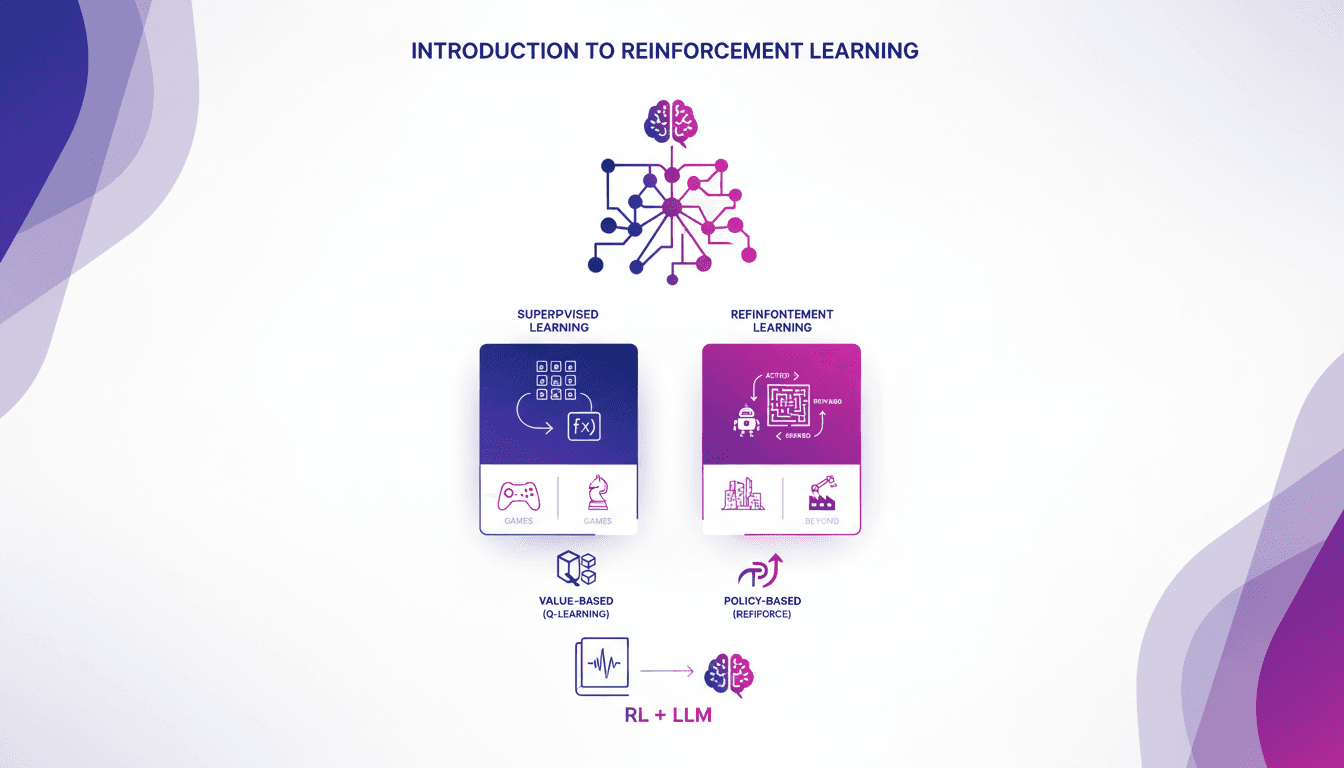
Practical Intro to Reinforcement Learning
I remember the first time I stumbled upon reinforcement learning. It felt like unlocking a new level in a game, where algorithms learn by trial and error, just like us. Unlike supervised learning, RL doesn't rely on labeled datasets. It learns from the consequences of its actions. First, I'll compare RL to supervised learning, then dive into its real-world applications, especially in games. I'll walk you through value-based methods like Q-learning and policy-based methods, showing how these approaches are transforming massive language models. In the end, you'll see how three key ways of using RL to fine-tune large language models deliver impressive results.
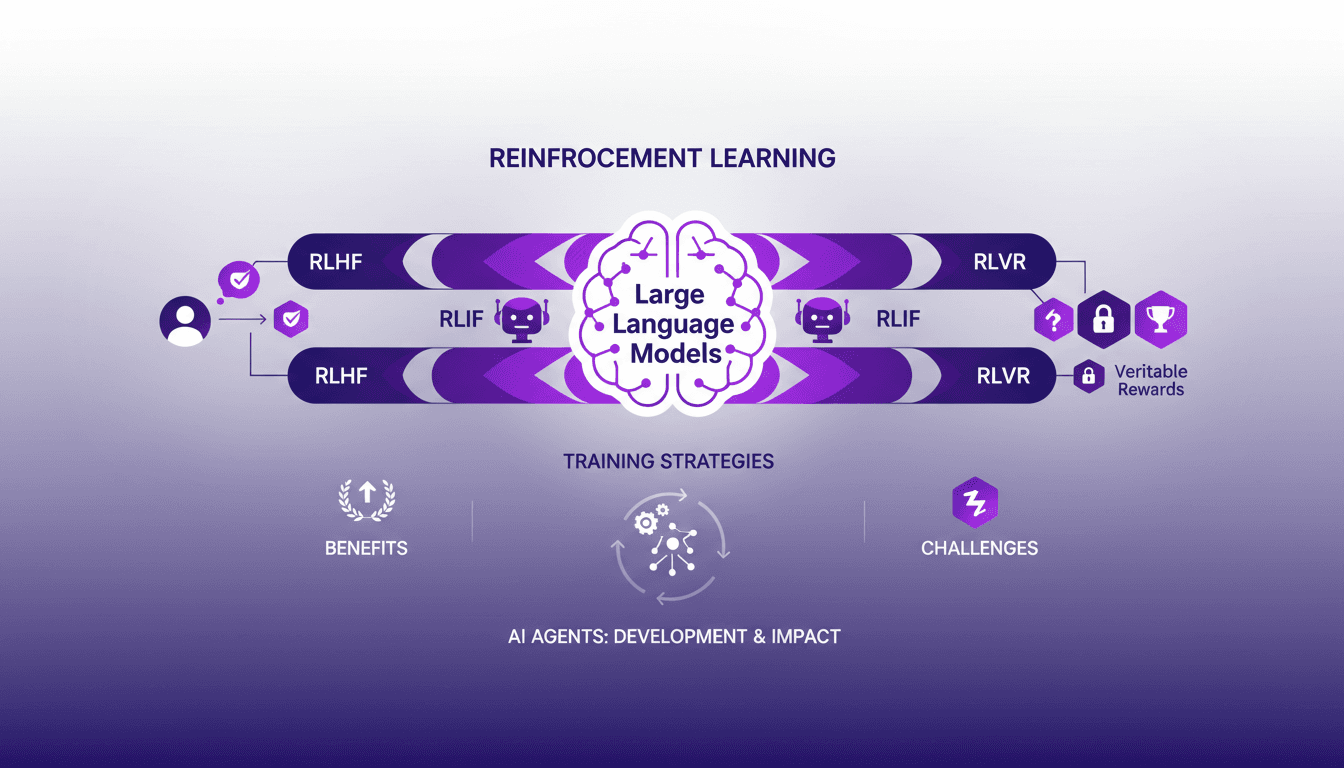
Reinforcement Learning for LLMs: New AI Agents
I remember the first time I integrated reinforcement learning into training large language models (LLMs). It was 2022, and with the development of ChatGPT fresh in my mind, I realized this was a real game-changer for AI agents. But be careful—there are trade-offs to consider. Reinforcement learning is revolutionizing how we train LLMs, offering new ways to enhance AI agents. In this article, I'll take you through my journey with RL in LLMs, sharing practical insights and lessons learned. I'm diving into reinforcement learning with human feedback (RLHF), AI feedback (RLIF), and verifiable rewards (RLVR). Get ready to explore how these approaches are transforming the way we design and train AI agents.
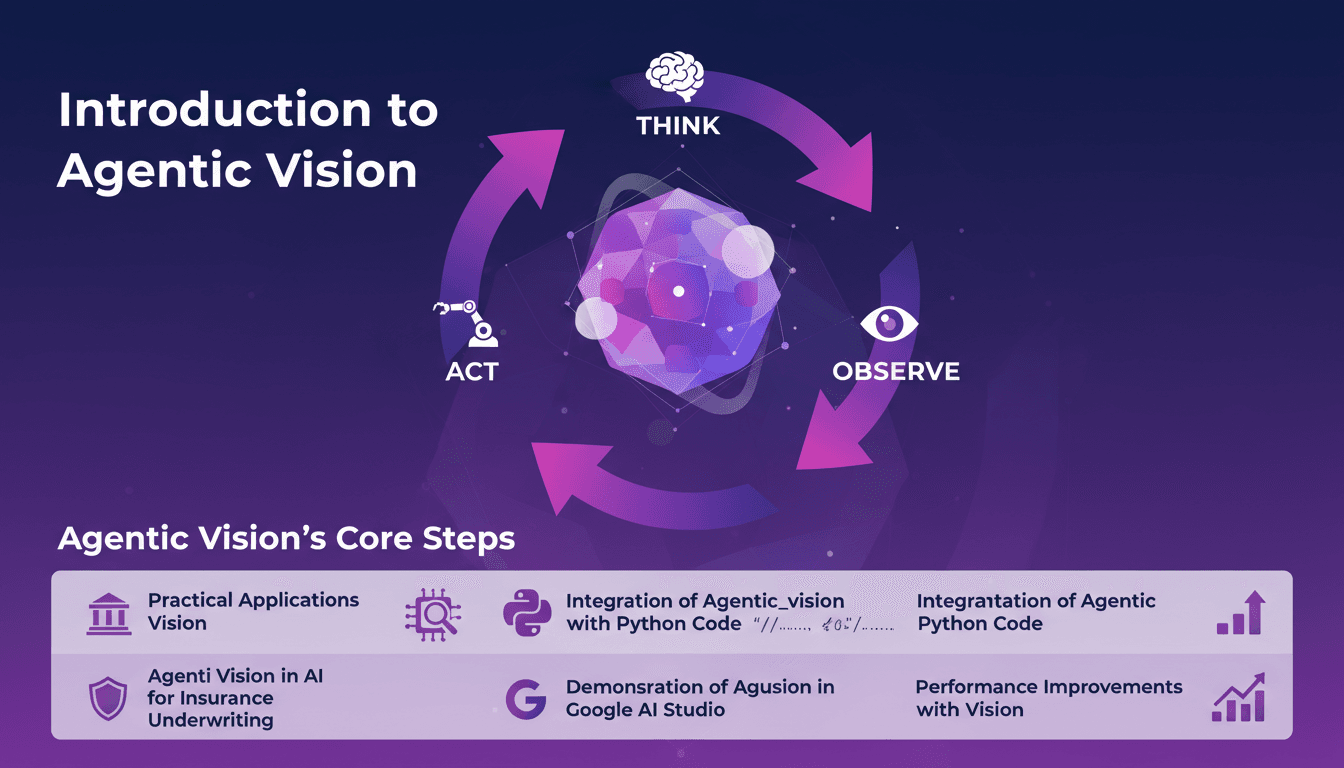
Agentic Vision: Boost AI with Python Integration
I remember the first time I stumbled upon Agentic Vision. It was like a light bulb moment, realizing how the Think, Act, Observe framework could revolutionize my AI projects. I integrated this approach into my workflows, especially for insurance underwriting, and the performance leaps were remarkable. Agentic Vision isn't just another AI buzzword. It's a practical framework that can truly boost your AI models, especially when paired with Python. Whether you're in insurance or any other field, understanding this can save you time and increase efficiency. In this video, I'll walk you through how I applied Agentic Vision with Python, and the performance improvements I witnessed, especially in Google AI Studio.
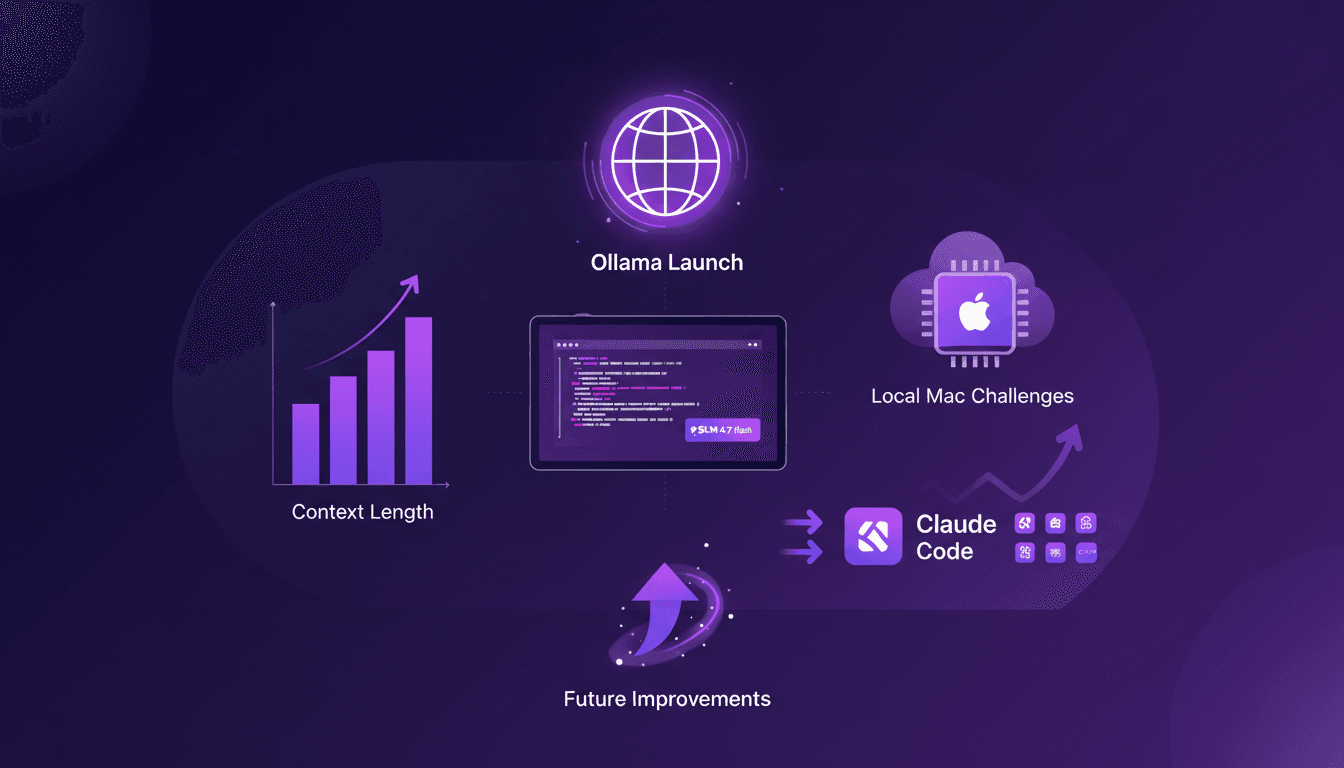
Ollama Launch: Tackling Mac Challenges
I remember the first time I fired up Ollama Launch on my Mac. It was like opening a new toolbox, gleaming with tools I was eager to try out. But the real question is how these models actually perform. In this article, we'll dive into Ollama Launch features, put the GLM 4.7 flash model through its paces, and see how Claude Code stacks up. We'll also tackle the challenges of running these models locally on a Mac and discuss potential improvements. If you've ever tried running a 30-billion parameter model with a 64K context length, you know what I'm talking about. So, ready to tackle the challenge?
Building Apps in ChatGPT: A Practical Guide
I’ve been knee-deep in the OpenAI ecosystem, and building apps in ChatGPT is like crafting a dynamic espresso shot—fast, efficient, and incredibly rewarding. With Codeex and MCP, I streamline the entire process. OpenAI's tools are game changers for developers eager to integrate AI into their apps. After hours in the trenches, today I'm sharing my workflow that makes app building not just feasible but efficient. From leveraging the OpenAI SDK to a live app creation demo, we’ll cover it all. I promise you, in two minutes, Codeex will already give you a starting scaffold.